KM-dcserver
IP address :
192.168.1.2
255.255.255.0
192.168.1.3
DNS:192.168.1.2
KM-dcbackup
IP address :
192.168.1.3
255.255.255.0
DNS:192.168.1.2
Sunday, December 12, 2010
Sunday, November 14, 2010
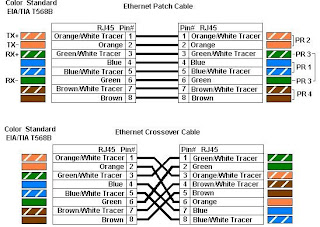
Standar colour coding for Cat5/6
WIRING STANDARD
PIN
WIRE COLOUR
1
White w/Orange Stripe
2
Orange w/White Stripe
3
White w/Green Stripe
4
Blue w/White Stripe
5
White w/Blue Stripe
6
Green w/White Stripe
7
White w/Brown Stripe
8
Brown w/White Stripe
PIN
WIRE COLOUR
1
White w/Orange Stripe
2
Orange w/White Stripe
3
White w/Green Stripe
4
Blue w/White Stripe
5
White w/Blue Stripe
6
Green w/White Stripe
7
White w/Brown Stripe
8
Brown w/White Stripe
Friday, November 12, 2010
How to reinstall the Smart Card service on Windows XP
How to reinstall the Smart Card service on Windows XP
If you're looking for a way to re-install the smart card service on Windows XP, this story is your new best friend!
Summary
Prepare a Windows XP installation disc
Download WinXP-scardsvr-install.zip
Read the included readme.txt
Examine install.bat in order to see what it does
Run the BAT file
Steps 3 and 4 are optional, but if you're someone who tinkers with the service, I'm sure you want to know what's in there.
Explanations
First of all you should make sure the service is completely removed. sc delete scardsvr is the standard and official way to remove the service (it is interesting that Microsoft provides a way to remove a service, but there is no known mechanism to re-install one).
Copy scardsvr.inf to %windir%\inf
Run sysocmgr.exe /i:caller.inf, this will invoke a wizard that will use the data inside scardsvr.inf to perform various actions (such as modifying registry keys, and copying files)
Uncheck Smart card service and press Next to remove the files and registry entries
Run the command again, the same window will be shown, check Smart card service and press Next (you will be asked to insert the Windows XP installation CD)
Perform a system restart, after checking the service manager (by running services.msc) and making sure the Smart card service startup is set to Automatic
If you examine scardsvr.inf you will see that it contains references to a list of files and registry keys. These actions could be performed manually, the effect would be the same; but using an .inf file is much easier.
If you're looking for a way to re-install the smart card service on Windows XP, this story is your new best friend!
Summary
Prepare a Windows XP installation disc
Download WinXP-scardsvr-install.zip
Read the included readme.txt
Examine install.bat in order to see what it does
Run the BAT file
Steps 3 and 4 are optional, but if you're someone who tinkers with the service, I'm sure you want to know what's in there.
Explanations
First of all you should make sure the service is completely removed. sc delete scardsvr is the standard and official way to remove the service (it is interesting that Microsoft provides a way to remove a service, but there is no known mechanism to re-install one).
Copy scardsvr.inf to %windir%\inf
Run sysocmgr.exe /i:caller.inf, this will invoke a wizard that will use the data inside scardsvr.inf to perform various actions (such as modifying registry keys, and copying files)
Uncheck Smart card service and press Next to remove the files and registry entries
Run the command again, the same window will be shown, check Smart card service and press Next (you will be asked to insert the Windows XP installation CD)
Perform a system restart, after checking the service manager (by running services.msc) and making sure the Smart card service startup is set to Automatic
If you examine scardsvr.inf you will see that it contains references to a list of files and registry keys. These actions could be performed manually, the effect would be the same; but using an .inf file is much easier.
Saturday, November 6, 2010
Steps for unread mails as read mails in Gmail
Over a period of time you may have tons of unread emails in your Gmail Inbox, most of these emails may be months or years old and navigating to each of these messages and marking them as read can be time consuming.
Here are three simple steps in which you can mark all the mails in Gmail
as read without having to visit each and every individual mail.
Also See: Searching for emails received in particular time frames.
Step 1: Search for Mails Which are Unread
The unread emails in Gmail are marked with the “unread” label, so a basic search for “label:unread” should display all the emails which are unread, you can also use this trick in combination with searching emails within particular time frames to only view unread emails that were received between certain dates.
Step 2: Select All the Emails in the Search Results
Once the search result
is displayed, click on the select All link to select the messages on the page.
Once you have clicked on the all link messages on the current page will be selected, if there are more than one pages with unread mails, you will see a additional message asking you to select all the messages that match this search, click on the link.
Clicking on this link should select all the unread messages.
Step 3: Mark all Messages as Read
Once you have selected all the messages, you can mark them as read by selecting the option from More Actions drop down list.
Selecting the mark as read option will show you a JavaScript alert since the actions span multiple pages, simple click on Ok to continue.
That’s it, your unread message count should drop to zero with this trick, rinse and repeat whenever your message count goes out of bounds.
Technorati Tags: tips and tricks,how to,gmail unread emails,mark emails read,gmail
Here are three simple steps in which you can mark all the mails in Gmail
as read without having to visit each and every individual mail.
Also See: Searching for emails received in particular time frames.
Step 1: Search for Mails Which are Unread
The unread emails in Gmail are marked with the “unread” label, so a basic search for “label:unread” should display all the emails which are unread, you can also use this trick in combination with searching emails within particular time frames to only view unread emails that were received between certain dates.
Step 2: Select All the Emails in the Search Results
Once the search result
is displayed, click on the select All link to select the messages on the page.
Once you have clicked on the all link messages on the current page will be selected, if there are more than one pages with unread mails, you will see a additional message asking you to select all the messages that match this search, click on the link.
Clicking on this link should select all the unread messages.
Step 3: Mark all Messages as Read
Once you have selected all the messages, you can mark them as read by selecting the option from More Actions drop down list.
Selecting the mark as read option will show you a JavaScript alert since the actions span multiple pages, simple click on Ok to continue.
That’s it, your unread message count should drop to zero with this trick, rinse and repeat whenever your message count goes out of bounds.
Technorati Tags: tips and tricks,how to,gmail unread emails,mark emails read,gmail
Network settings for VMWare Fusion

Network settings for VMWare Fusion
Posted October 6th, 2010 by David Gabbe
in
• Bridged
• Fusion
• NAT
• network
• VMWare
By default VMWare Fusion sets the network setting to NAT (Share the Mac's network connection). The advantage of this setting is as your Mac switches networks, your virtual PC (guest operating system) will switch too.
However, some Windows programs are designed a bit differently, such as the admin software that controls our phone system and it expects to communicate directly with the physical network. It wants Bridged (Connect directly to the physical network).
A good hint to try Bridged is when you get a cryptic error message about not being able to connect or detect some device. Scanners and faxes are likely to prefer a Bridged connection as well.
Wednesday, September 22, 2010
Server Related Questions
1. How to check disk performance? How to troubleshoot that problem? What is the procedure?
2. How to delete software errors? What is that?
3. if the server has slow how to check the server performance?
How to check server performance what is the procedure?
4. if the server is down, how to bring up the server?
5. if one server is down, whenever restart the machine we get ok prompt what is the problem?
6. one server is down it doen't display anything what you do?
7. in vcs, which network[private or public] channel bandwidth is high?
8. why we r going to freezing service group and system, what are the freezing steps & how to freezing service group?
9. whenever we give #metastat cmd in svm, it display output "need to maintain" state, what u do?
10. in solaris file sysrm is full what u do?
11. whenever install patch cluster, system will be restart what is the problem?
12. how to check or see device port number?
13. how to know how many samba users in solaris?
14. how to merge solaris partition?
15. diff between /etc/inetd and smf?
16. how to set kernal parameters in solaris 10&9?
17. how do I disable dmp?
18. how to add a new host to DNS?
19. what is the diff between LLT,GAB&TCP/IP?
20. what is vcs seeding & jeopardy & purpose?
21. I am using solaris box, I need to delete a file from path /usr/tmp/ which r older than 24 hours?
22. which server we can update first in DNS?
2. How to delete software errors? What is that?
3. if the server has slow how to check the server performance?
How to check server performance what is the procedure?
4. if the server is down, how to bring up the server?
5. if one server is down, whenever restart the machine we get ok prompt what is the problem?
6. one server is down it doen't display anything what you do?
7. in vcs, which network[private or public] channel bandwidth is high?
8. why we r going to freezing service group and system, what are the freezing steps & how to freezing service group?
9. whenever we give #metastat cmd in svm, it display output "need to maintain" state, what u do?
10. in solaris file sysrm is full what u do?
11. whenever install patch cluster, system will be restart what is the problem?
12. how to check or see device port number?
13. how to know how many samba users in solaris?
14. how to merge solaris partition?
15. diff between /etc/inetd and smf?
16. how to set kernal parameters in solaris 10&9?
17. how do I disable dmp?
18. how to add a new host to DNS?
19. what is the diff between LLT,GAB&TCP/IP?
20. what is vcs seeding & jeopardy & purpose?
21. I am using solaris box, I need to delete a file from path /usr/tmp/ which r older than 24 hours?
22. which server we can update first in DNS?
Wednesday, September 1, 2010
Oracle -10G Installations
ProgrammerWorld.NET
* Reviews
* Parent Site
* Amazon Deals
* Advertise
* About us
Search
Web This Site
Submit search form
Database
* Offer for Programmerworld users 40% off
* Installing Oracle 10g – step by step guide
* SQL Interview Questions and Answers
* FAQs about MS-SQl server
Main Menu
* Money Making Tips
* Microsoft Windows
* Web Publishing
* The Web
* Miscellaneous
* VoIP
* Database
* Programming
* Coolest Gadgets
* Networking / Hardware
* Resume Tips
* Interview Tips
* Career Tips
* PC
* Linux/Unix
* Fun & Time-pass Stuff
* Reviews Section
* SiteMap
Sister Sites
* ProgrammerWorld
* DevelopersVoice
* Faq.ProgrammerWorld.Net
* Health.ProgrammerWorld.Net
* Tips.DevelopersVoice.Com
Installing Oracle 10g – step by step guide
Introduction:
This article is a step-by-step instruction for those who want to install Oracle 10g database on their computer. This document provides guidelines to install Oracle 10g database on Microsoft Windows environment. If you use other operating system other than Microsoft Windows, the process is not too much different from that of Microsoft Windows, since Oracle uses Oracle Universal Installer to install its software.
For more information about installing Oracle 10g under operating systems other than Microsoft Windows, please refer to this URL :
http://www.oracle.com/pls/db102/homepage
How to get Oracle 10g :
You can download Oracle 10g database from www.oracle.com. You must registered and create an account before you can download the software. The example in this document uses Oracle Database 10g Release 2 (10.2.0.1.0) for Microsoft Windows.
How to uninstall Oracle database software :
1. Uninstall all Oracle components using the Oracle Universal Installer (OUI).
2. Run regedit.exe and delete the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/ SOFTWARE/ORACLE key. This contains registry entire for all Oracle products.
3. Delete any references to Oracle services left behind in the following part of the registry: HKEY LOCAL MACHINE/ SYSTEM/ CurrentControlsSet/ Services/Ora*. It should be pretty obvious which ones relate to Oracle
4. Reboot your machine.
5. Delete the C: \Oracle directory, or whatever directory is your Oracle_Base.
6. Delete the C:\Program Files \Oracle directory.
7. Empty the contents of your c:\temp directory.
8. Empty your recycle bin.
Installing Oracle 10g database software :
1. Insert Oracle CD , the autorun window opens automatically. If you are installing from network or hard disk, click setup.exe in the installation folder.
2. The Oracle Universal Installer (OUI) will run and display the Select Installation Method Window.
oracle10g installation
3. Choose Basic Installation:
Select this option to quickly install Oracle Database 10g. This method requires minimal user input. It installs the software and optionally creates a general-purpose database based on the information you provide.
For basic installation, you specify the following:
Oracle Home Location — Enter the directory in which to install the Oracle Database 10g software. You must specify a new Oracle home directory for each new installation of Oracle Database 10g. Use the default value, which is :
c:\oracle\product\10.2.0\db_1
Installation Type — Select Enterprise Edition :
If you have limited space, select standard edition. Personal edition installs the same software as the Enterprise Edition, but supports only a single-user development and deployment environment.
Create Starter Database — Check this box to create a database during installation. Oracle recommends that you create a starter database for first Create Starter Database — time installations. Choose a Global Database Name, like cs157b, or just use the default value.
Type a password. Don’t lose this password, since you will need it to connect to the database server.
Click next
4. The Product-Specific Prerequisite Checks window appears: Click next
oracle10g installation
5. A summary screen appears showing information such as your global settings, space requirements and the new products to be installed. Click Install to start the installation..
6. The Install window appears showing installation progress.
oracle10g_installation
7. At the end of the installation phase, the Configuration Assistants window appears. This window lists the configuration assistants that are started automatically.
If you are creating a database, then the Database Configuration Assistant starts automatically in a separate window.
oracle 10g installation
oracle 10g installation
At the end of database creation, you are prompted to unlock user accounts to make the accounts accessible. The SYS and SYSTEM accounts are already unlocked. Click OK to bypass password management.
oracle 10g installation
Note: Oracle 10g still keeps scott / tiger username and password (UID=scott, PWD=tiger) from the old version of oracle. In the old version of oracle, scott/tiger user ID is available by default, but not in oracle 10g. If you want to use scott /tiger account, you must unlock it by clicking “Password Management” at the last window.
Password Management window will appear like the one shown below. Find the user name “Scott” and uncheck the “Lock Account?” column for the user name.
8. Your installation and database creation is now complete. The End of Installation window displays several important URLs, one of which is for Enterprise Manager.
oracle 10g installation
9. You can navigate to this URL in your browser and log in as the SYS user with the associated password, and connect as SYSDBA. You use Enterprise Manager to perform common database administration tasks
Note : you can access Oracle Enterprise Manager using browser by typing the URL shown above in your browser. Instead of typing the IP address, you can also access the Enterprise Manager by typing http://localhost:1158/em or “http://[yourComputerName]:1158/em” or by clicking “Start >> All Programs >> Oracle – [YourOracleHome_home1] >> Database Control – [yourOracleID]” in Windows menu.
By default, use user ID “SYSTEM”, with the password that you have chosen at the beginning of installation, to connect to database, SQLPlus, etc. If you want to use other user ID, you may create a new user .
AddThis
Contact or send us suggestions at : Admin@ProgrammerWorld.NET
For any business and Advertisement related queries contact us on : Admin@ProgrammerWorld.NET
Copyright © 2009 ProgrammerWorld.NET. All Rights Reserved.
Ads By infinityads.comClose
* Reviews
* Parent Site
* Amazon Deals
* Advertise
* About us
Search
Web This Site
Submit search form
Database
* Offer for Programmerworld users 40% off
* Installing Oracle 10g – step by step guide
* SQL Interview Questions and Answers
* FAQs about MS-SQl server
Main Menu
* Money Making Tips
* Microsoft Windows
* Web Publishing
* The Web
* Miscellaneous
* VoIP
* Database
* Programming
* Coolest Gadgets
* Networking / Hardware
* Resume Tips
* Interview Tips
* Career Tips
* PC
* Linux/Unix
* Fun & Time-pass Stuff
* Reviews Section
* SiteMap
Sister Sites
* ProgrammerWorld
* DevelopersVoice
* Faq.ProgrammerWorld.Net
* Health.ProgrammerWorld.Net
* Tips.DevelopersVoice.Com
Installing Oracle 10g – step by step guide
Introduction:
This article is a step-by-step instruction for those who want to install Oracle 10g database on their computer. This document provides guidelines to install Oracle 10g database on Microsoft Windows environment. If you use other operating system other than Microsoft Windows, the process is not too much different from that of Microsoft Windows, since Oracle uses Oracle Universal Installer to install its software.
For more information about installing Oracle 10g under operating systems other than Microsoft Windows, please refer to this URL :
http://www.oracle.com/pls/db102/homepage
How to get Oracle 10g :
You can download Oracle 10g database from www.oracle.com. You must registered and create an account before you can download the software. The example in this document uses Oracle Database 10g Release 2 (10.2.0.1.0) for Microsoft Windows.
How to uninstall Oracle database software :
1. Uninstall all Oracle components using the Oracle Universal Installer (OUI).
2. Run regedit.exe and delete the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/ SOFTWARE/ORACLE key. This contains registry entire for all Oracle products.
3. Delete any references to Oracle services left behind in the following part of the registry: HKEY LOCAL MACHINE/ SYSTEM/ CurrentControlsSet/ Services/Ora*. It should be pretty obvious which ones relate to Oracle
4. Reboot your machine.
5. Delete the C: \Oracle directory, or whatever directory is your Oracle_Base.
6. Delete the C:\Program Files \Oracle directory.
7. Empty the contents of your c:\temp directory.
8. Empty your recycle bin.
Installing Oracle 10g database software :
1. Insert Oracle CD , the autorun window opens automatically. If you are installing from network or hard disk, click setup.exe in the installation folder.
2. The Oracle Universal Installer (OUI) will run and display the Select Installation Method Window.
oracle10g installation
3. Choose Basic Installation:
Select this option to quickly install Oracle Database 10g. This method requires minimal user input. It installs the software and optionally creates a general-purpose database based on the information you provide.
For basic installation, you specify the following:
Oracle Home Location — Enter the directory in which to install the Oracle Database 10g software. You must specify a new Oracle home directory for each new installation of Oracle Database 10g. Use the default value, which is :
c:\oracle\product\10.2.0\db_1
Installation Type — Select Enterprise Edition :
If you have limited space, select standard edition. Personal edition installs the same software as the Enterprise Edition, but supports only a single-user development and deployment environment.
Create Starter Database — Check this box to create a database during installation. Oracle recommends that you create a starter database for first Create Starter Database — time installations. Choose a Global Database Name, like cs157b, or just use the default value.
Type a password. Don’t lose this password, since you will need it to connect to the database server.
Click next
4. The Product-Specific Prerequisite Checks window appears: Click next
oracle10g installation
5. A summary screen appears showing information such as your global settings, space requirements and the new products to be installed. Click Install to start the installation..
6. The Install window appears showing installation progress.
oracle10g_installation
7. At the end of the installation phase, the Configuration Assistants window appears. This window lists the configuration assistants that are started automatically.
If you are creating a database, then the Database Configuration Assistant starts automatically in a separate window.
oracle 10g installation
oracle 10g installation
At the end of database creation, you are prompted to unlock user accounts to make the accounts accessible. The SYS and SYSTEM accounts are already unlocked. Click OK to bypass password management.
oracle 10g installation
Note: Oracle 10g still keeps scott / tiger username and password (UID=scott, PWD=tiger) from the old version of oracle. In the old version of oracle, scott/tiger user ID is available by default, but not in oracle 10g. If you want to use scott /tiger account, you must unlock it by clicking “Password Management” at the last window.
Password Management window will appear like the one shown below. Find the user name “Scott” and uncheck the “Lock Account?” column for the user name.
8. Your installation and database creation is now complete. The End of Installation window displays several important URLs, one of which is for Enterprise Manager.
oracle 10g installation
9. You can navigate to this URL in your browser and log in as the SYS user with the associated password, and connect as SYSDBA. You use Enterprise Manager to perform common database administration tasks
Note : you can access Oracle Enterprise Manager using browser by typing the URL shown above in your browser. Instead of typing the IP address, you can also access the Enterprise Manager by typing http://localhost:1158/em or “http://[yourComputerName]:1158/em” or by clicking “Start >> All Programs >> Oracle – [YourOracleHome_home1] >> Database Control – [yourOracleID]” in Windows menu.
By default, use user ID “SYSTEM”, with the password that you have chosen at the beginning of installation, to connect to database, SQLPlus, etc. If you want to use other user ID, you may create a new user .
AddThis
Contact or send us suggestions at : Admin@ProgrammerWorld.NET
For any business and Advertisement related queries contact us on : Admin@ProgrammerWorld.NET
Copyright © 2009 ProgrammerWorld.NET. All Rights Reserved.
Ads By infinityads.comClose
Saturday, August 7, 2010
Microsoft Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide Microsoft Corporation Author: Anita Taylor Editor: Theresa Haynie Abstract
This guide provides detailed instructions for installing Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2) using either Windows Server Manager or the WSUSSetup.exe file. This guide also contains basic setup instructions for WSUS 3.0 SP2 using either Windows Server Manager or the WSUS Server Configuration Wizard.
Copyright Notice Information in this document, including URL and other Internet Web site references, is subject to change without notice. Unless otherwise noted, the companies, organizations, products, domain names, e-mail addresses, logos, people, places, and events depicted in examples herein are fictitious. No association with any real company, organization, product, domain name, e-mail address, logo, person, place, or event is intended or should be inferred. Complying with all applicable copyright laws is the responsibility of the user. Without limiting the rights under copyright, no part of this document may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise), or for any purpose, without the express written permission of Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft may have patents, patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights covering subject matter in this document. Except as expressly provided in any written license agreement from Microsoft, the furnishing of this document does not give you any license to these patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property. © 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft, Active Directory, ActiveX, Authenticode, Excel, InfoPath, Internet Explorer, MSDN, Outlook, Visual Studio, Win32, Windows, Windows Server, and Windows Vista are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
Contents
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide ................................................... 5
Additional References .............................................................................................................. 5
Step 1: Confirm WSUS 3.0 SP2 Installation Requirements .......................................................... 5
Server Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing WSUS 3.0 SP2 ............................. 6
Client Software Requirements .................................................................................................. 6
Permissions ............................................................................................................................. 6
Preparing to Install WSUS 3.0 SP2 .......................................................................................... 6
Next Step ................................................................................................................................ 7
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................... 7
Step 2: Install WSUS Server or Administration Console ............................................................... 7
If You Are Using Server Manager ............................................................................................. 8
If You Are Using the WSUSSetup.exe File ............................................................................... 8
Using the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Setup Wizard ................................................................................... 8
Next Step ............................................................................................................................... 11
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................. 11
Step 3: Configure the Network Connections............................................................................... 11
Next Step ............................................................................................................................... 14
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................. 15
Step 4: Configure Updates and Synchronization ........................................................................ 15
Step 4 Procedures ................................................................................................................. 15
If You Are Using the Windows Server Update Services Configuration Wizard ......................... 15
If You Are Using the WSUS Administration Console ............................................................... 17
Next Step ............................................................................................................................... 18
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................. 18
Step 5: Configure Client Updates............................................................................................... 18
Step 5 Procedures ................................................................................................................. 19
Next Step ............................................................................................................................... 20
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................. 20
Step 6: Configure Computer Groups .......................................................................................... 20
Step 6 Procedures ................................................................................................................. 21
Next Step ............................................................................................................................... 21
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................. 21
Step 7: Approve and Deploy WSUS Updates............................................................................. 22
Step 7 Procedures ................................................................................................................. 22
Additional resources............................................................................................................... 23
5
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2) provides a comprehensive solution for managing updates to your network. This guide provides instructions for the basic installation and deployment tasks by using WSUS 3.0 SP2 on your network. This guide contains the following sections:
Step 1: Confirm WSUS 3.0 SP2 Installation Requirements
Step 2: Install WSUS Server or Administration Console
Step 3: Configure the Network Connections
Step 4: Configure Updates and Synchronization
Step 5: Configure Client Updates
Step 6: Configure Computer Groups
Step 7: Approve and Deploy WSUS Updates
Additional References
WSUS 3.0 SP2 is a feature-rich update management solution. For complete information about installing and using WSUS, refer to the following Web sites:
The WSUS Deployment Guide at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139832.
The WSUS Operations Guide at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139838.
The WSUS Release Notes at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139840.
Step 1: Confirm WSUS 3.0 SP2 Installation Requirements
Before you install or upgrade to Windows Server Upgrade Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2), confirm that both the server and the client computers meet the WSUS 3.0 SP2 system requirements and confirm that you have the necessary permissions to complete the installation.
6
Server Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing WSUS 3.0 SP2
1. Confirm that the server meets the WSUS 3.0 SP2 system requirements for hardware, operating system, and other required software. System requirements are listed in the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Release Notes at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139840. If you are using Server Manager to install the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Server, you can confirm that you meet the software requirements by following the steps in the “Preparing to Install WSUS 3.0 SP2” section. 2. If you install roles or software updates that require you to restart the server when installation is complete, then restart the server before you install WSUS 3.0 SP2.
Client Software Requirements
Automatic Updates is the client of WSUS 3.0. Automatic Updates has no hardware requirements other than being connected to the network.
1. Confirm that computer on which you are installing Automatic Updates meets the WSUS 3.0 SP2 system requirements for Client computers. System requirements are listed in the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Release Notes at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139840. 2. If you install software updates that require you to restart the computer, restart it before you install WSUS 3.0 SP2.
Permissions
The following permissions are required for the specified users and directories: 1. The NT Authority\Network Service account must have Full Control permission for the following folders so that the WSUS Administration snap-in displays correctly: %windir%\Microsoft .NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\Temporary ASP.NET Files %windir%\Temp 2. Confirm that the account that you plan to use to install WSUS 3.0 SP2 is a member of the Local Administrators group.
Preparing to Install WSUS 3.0 SP2
If you are running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 SP2, you can install WSUS 3.0 SP2 from Server Manager. If you are using another supported operating system, or installing only the WSUS Administration Console, go to the next section of this guide to install WSUS 3.0 SP2 by using the WSUSSetup.exe file.
1. Log on to the server on which you plan to install WSUS 3.0 SP2 by using an account that
To prepare to install the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Server by using Server Manager
7
is a member of the Local Administrators group. 2. Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager. 3. In the right side pane of the Server Manager window, in the Roles Summary section, click Add Roles. 4. If the Before You Begin page appears, click Next. 5. On the Select Server Roles page, confirm that Application Server and Web Server (IIS) are selected. If they have been selected, use the remainder of this step to confirm that the required role services are selected. Otherwise, install Application Server and Web Server (IIS) as follows. a. On the Select Server Roles page, select Application Server and Web Server (IIS). Click Next. b. If you are installing Application Role Services, on the Application Server page, click Next. On the Application Server Role Services page, accept the default settings, and then click Next. c. If you are installing Web Server IIS, on the Web Server (IIS) page, click Next. On the Web Server (IIS) Role Services page, in addition to the default settings, select ASP.NET, Windows Authentication, Dynamic Content Compression, and IIS 6 Management Compatibility. If the Add Roles Wizard window appears, click Add Required Role Services. Click Next. d. On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install. e. On the Installation Results page, confirm that an “Installation succeeded” message appears for the role services that you installed in this step, and then click Close.
Next Step
Step 2: Install WSUS Server or Administration Console
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Step 2: Install WSUS Server or Administration Console
After you make sure that the server meets the minimum system requirements and that the necessary account permissions were granted, you are ready to install Windows Server Upgrade Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2). Start the installation of WSUS 3.0 SP2 by using the applicable procedure for your operating system and kind of installation (by using either Server Manager or the WSUSSetup.exe file).
8
If You Are Using Server Manager
1. Log on to the server on which you plan to install WSUS 3.0 SP2 by using an account that is a member of the local Administrators group. 2. Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager. 3. In the right side pane of the Server Manager window, in the Roles Summary section, click Add Roles. 4. If the Before You Begin page appears, click Next. 5. On the Select Server Roles page, select Windows Server Update Services. 6. On the Windows Server Update Services page, click Next. 7. On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install. 8. When the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Setup Wizard is started, skip the next section and see the “To continue installing WSUS 3.0 SP2” procedure.
If You Are Using the WSUSSetup.exe File
1. Log on to the server on which you plan to install WSUS 3.0 SP2 by using an account that is a member of the Local Administrators group. 2. Double-click the WSUSSetup.exe installer file. 3. When the Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Setup Wizard is started, see the “To continue installing WSUS 3.0 SP2” procedure.
Using the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Setup Wizard
The WSUS Setup Wizard is launched from Server Manager or from the WSUSSetup.exe file.
1. On the Welcome page of the Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Setup Wizard, click Next. 2. On the Installation Mode Selection page, select Full server installation including Administration Console if you want to install the WSUS server on this computer, or Administration Console only if you want to install the administration console only. 3. On the License Agreement page, read the terms of the license agreement, click I accept the terms of the License agreement, and then click Next.
4. You can specify where clients get updates on the Select Update Source page of the
To start the installation of WSUS 3.0 SP2 Server by using Server Manager
To start the installation of WSUS 3.0 SP2 Server or the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Administration Console by using the WSUSSetup.exe file
To continue installing WSUS 3.0 SP2
9
installation wizard. By default, the Store updates locally check box is selected and updates will be stored on the WSUS server in the location that you specify. If you clear the Store updates locally check box, client computers obtain approved updates by connecting to Microsoft Update. Make your selection, and then click Next.
5. On the Database Options page, select the software that is used to manage the WSUS 3.0 database. By default, the installation wizard offers to install Windows Internal Database. If you do not want to use Windows Internal Database, provide an instance of Microsoft SQL Server for WSUS to use by selecting Use an existing database on this server or Use an existing database server on a remote computer. Type the instance name in the applicable box. The instance name should appear as\, where serverName is the name of the server and instanceName is the name of the SQL instance. Make your selection, and then click Next.
10
6. If you have opted to connect to a SQL Server, on the Connecting to SQL Server Instance page, WSUS will try to connect to the specified instance of SQL Server. When it has connected successfully, click Next to continue. 7. On the Web Site Selection page, specify the Web site that WSUS will use. If you want to use the default Web site on port 80, select Use the existing IIS Default Web site. If you already have a Web site on port 80, you can create an alternate site on port 8530 or 8531 by selecting Create a Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Web site. Click Next.
11
8. On the Ready to Install Windows Server Update Services page, review the selections, and then click Next. 9. The final page of the installation wizard will let you know if the WSUS installation completed successfully. After you click Finish the configuration wizard will start.
Next Step
Step 3: Configure the Network Connections
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Step 3: Configure the Network Connections
After you install Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2), the configuration wizard will launch automatically. You can also run the wizard later through the Options page of the WSUS Administration Console.
12
Before you start the configuration process, be sure that you know the answers to the following questions: 1. Is the server's firewall configured to allow clients to access the server? 2. Can this computer connect to the upstream server (such as Microsoft Update)? 3. Do you have the name of the proxy server and the user credentials for the proxy server, if you need them? By default, WSUS 3.0 SP2 is configured to use Microsoft Update as the location from which to obtain updates. If you have a proxy server on the network, you can configure WSUS 3.0 SP2 to use the proxy server. If there is a corporate firewall between WSUS and the Internet, you might have to configure the firewall to ensure that WSUS can obtain updates.
Note Although Internet connectivity is required to download updates from Microsoft Update, WSUS offers you the ability to import updates onto networks that are not connected to the Internet. Step 3 contains the following procedures: Configure your firewall. Specify the way this server will obtain updates (either from Microsoft Update or from another WSUS server). Configure proxy server settings, so that WSUS can obtain updates.
If there is a corporate firewall between WSUS and the Internet, you might have to configure that firewall to ensure WSUS can obtain updates. To obtain updates from Microsoft Update, the WSUS server uses port 80 for HTTP protocol and port 443 for HTTPS protocol. This is not configurable. If your organization does not enable port 80 or port 443 to be open to all addresses, you can restrict access to only the following domains, so that WSUS and Automatic Updates can communicate with Microsoft Update: http://windowsupdate.microsoft.com http://*.windowsupdate.microsoft.com https://*.windowsupdate.microsoft.com http://*.update.microsoft.com https://*.update.microsoft.com http://*.windowsupdate.com http://download.windowsupdate.com http://download.microsoft.com http://*.download.windowsupdate.com http://wustat.windows.com
To configure your firewall
13
http://ntservicepack.microsoft.com
Note These instructions about how to configure the firewall are meant for a corporate firewall positioned between WSUS and the Internet. Because WSUS initiates all of its network traffic, you do not have to configure Windows Firewall on the WSUS server. Although the connection between Microsoft Update and WSUS requires ports 80 and 443 to be open, you can configure multiple WSUS servers to synchronize with a custom port. The next two procedures assume that you are using the Configuration Wizard. In a later section in this step, you will learn how to start the WSUS Administration snap-in and configure the server through the Options page.
1. From the configuration wizard, after joining the Microsoft Improvement Program, click Next to select the upstream server. 2. If you choose to synchronize from Microsoft Update, you are finished with the Options page. Click Next, or select Specify Proxy Server from the navigation pane. 3. If you choose to synchronize from another WSUS server, specify the server name and the port on which this server will communicate with the upstream server. 4. To use SSL, select the Use SSL when synchronizing update information check box. In that case the servers will use port 443 for synchronization. (Make sure that both this server and the upstream server support SSL.) 5. If this is a replica server, select the This is a replica of the upstream server check box. 6. At this point, you are finished with upstream server configuration. Click Next, or select Specify proxy server from the left navigation pane.
1. On the Specify Proxy Server page of the configuration wizard, select the Use a proxy server when synchronizing check box, and then type the proxy server name and port number (port 80 by default) in the corresponding boxes. 2. If you want to connect to the proxy server by using specific user credentials, select the Use user credentials to connect to the proxy server check box, and then type the user name, domain, and password of the user in the corresponding boxes. If you want to enable basic authentication for the user connecting to the proxy server, select the Allow basic authentication (password is sent in cleartext) check box. 3. At this point, you are finished with proxy server configuration. Click Next to go to the next page, where you can start to set up the synchronization process.
The following two procedures assume that you are using the WSUS Administration snap-in for configuration. These two procedures show how to start the WSUS Administration snap-in and configure the server from the Options page.
To specify the way this server will obtain updates
To configure proxy server settings
14
To start the WSUS Administration Console, click Start, point to All Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Windows Server Update Services 3.0.
Note In order to use all the features of the console, log on as a member of either the WSUS Administrators or the Local Administrators security groups on the server on which WSUS is installed. Members of the WSUS Reporters security group have read-only access to the console.
1. On the WSUS console, click Options in the left pane under the name of this server, and then click Update Source and Proxy Server in the middle pane. A dialog box will be displayed with Update Source and Proxy Server tabs. 2. In the Update Source tab, select the location from which this server will obtain updates. If you choose to synchronize from Microsoft Update (the default), you are finished with this wizard page. 3. If you choose to synchronize from another WSUS server, you have to specify the port on which the servers will communicate (the default is port 80). If you select a different port, you should ensure that both servers can use that port. 4. You may also specify whether to use SSL when synchronizing from the upstream WSUS server. In that case, the servers will use port 443 to synchronize from the upstream server. 5. If this server is a replica of the second WSUS server, select the This is a replica of the upstream server check box. In this case all updates must be approved on the upstream WSUS server only. 6. In the Proxy server tab, select the Use a proxy server when synchronizing check box, and then type the proxy server name and port number (port 80 by default) in the corresponding boxes. 7. If you want to connect to the proxy server by using specific user credentials, select the Use user credentials to connect to the proxy server check box, and then type the user name, domain, and password of the user in the corresponding boxes. If you want to enable basic authentication for the user connecting to the proxy server, select the Allow basic authentication (password in cleartext) check box. 8. Click OK to save these settings.
Next Step
Step 4: Configure Updates and Synchronization
To start the WSUS Administration Console
To specify an update source and proxy server
15
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Step 4: Configure Updates and Synchronization
This section describes how to configure a set of updates that you want to download by using Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2).
Step 4 Procedures
You can do these procedures by using either the WSUS Configuration Wizard or the WSUS Administration Console. 1. Save and download information about your upstream server and proxy server. 2. Choose the language of the updates. 3. Select the products for which you want to receive updates. 4. Choose the classifications of updates. 5. Specify the synchronization schedule for this server. After you configure the network connection, you can download updates by synchronizing the WSUS server. Synchronization begins when the WSUS server contacts Microsoft Update. After the WSUS makes contact, WSUS determines whether any new updates have been made available since the last time you synchronized. When you synchronize the WSUS server for the first time, all the updates are available and are ready for your approval for installation. The initial synchronization may take a long time. The procedures in this section describe synchronizing with the default settings. WSUS 3.0 SP2 also includes options that enable you to minimize bandwidth use during synchronization.
If You Are Using the Windows Server Update Services Configuration Wizard
In the step 3 procedures, you completed configuration of the upstream server and the proxy server. This next set of procedures starts on the Connect to Upstream Server page of that configuration wizard.
1. On the Connect to Upstream Server page of the configuration wizard, click the Start Connecting button. This both saves and uploads your settings and collects information about available updates.
To save and download your upstream server and proxy information
16
2. While the connection is being made, the Stop Connecting button will be available. If there are problems with the connection, click Stop Connecting, fix the problems, and restart the connection. 3. After the download has completed successfully, click Next.
1. The Choose Languages page lets you receive updates from all languages or from a subset of languages. Selecting a subset of languages will save disk space, but it is important to choose all of the languages that will be needed by all the clients of this WSUS server. If you choose to get updates only for specific languages, select Download updates only in these languages, and select the languages for which you want updates. 2. Click Next.
1. The Choose Products page lets you specify the products for which you want updates. Select product categories, such as Windows, or specific products, such as Windows Server 2008. Selecting a product category will cause all the products in that category to be selected. 2. Click Next.
1. The Choose Classifications page allows you to specify the update classifications you want to obtain. Choose all the classifications or a subset of them. 2. Click Next
1. On the Set Sync Schedule page, you choose whether to perform synchronization manually or automatically. If you choose Synchronize manually, you must start the synchronization process from the WSUS Administration Console. If you choose Synchronize automatically, the WSUS server will synchronize at set intervals. Set the time of the First synchronization and specify the number of Synchronizations per day that you want this server to perform. For example, if you specify that there should be four synchronizations per day, starting at 3:00 A.M., synchronizations will occur at 3:00 A.M., 9:00 A.M., 3:00 P.M., and 9:00 P.M. 2. Click Next.
3. On the Finished page, you can start the WSUS Administration Console by leaving the Launch the Windows Server Update Services Administrations snap-in check box
To choose update languages
To choose update products
To choose update classifications
To configure the synchronization schedule
17
selected, and you can start the first synchronization by leaving the Begin initial synchronization check box selected. 4. Click Finish.
Important You cannot save configuration changes that are made while the server is synchronizing. Wait until synchronization is finished and then make your changes.
If You Are Using the WSUS Administration Console
The following procedures explain how to perform the configuration steps by using the WSUS Administration Console.
1. In the Options panel, click Products and Classifications. A dialog box appears with Products and Classifications tabs. 2. In the Products tab, select the product category or specific products for which you want this server to receive updates, or else select All Products. 3. In the Classifications tab, select the update classifications you want, or else select All Classifications. 4. Click OK to save your selections.
1. In the Options panel, click Update Files and Languages. A dialog box appears with Update Files and Update Languages tabs. 2. In the Update Files tab, choose whether to Store update files locally on this server or to have all client computers install from Microsoft Update. If you decide to store update files on this server, you also decide whether to download only those updates that are approved or to download express installation files. 3. In the Update Languages tab, if you are storing update files locally, you choose to Download updates for all languages (the default), or to Download updates only in the specified languages. If this WSUS server has downstream servers, they will receive updates only in the languages specified by the upstream server. 4. Click OK to save these settings.
1. In the Options panel, click Synchronization Schedule.
2. In the Synchronization Schedule tab, you choose whether to perform synchronization
To choose products and update classifications
To choose update files and languages
To synchronize the WSUS server
18
manually or automatically. If you choose Synchronize manually, you will have to start the synchronization process from the WSUS Administration Console. If you choose Synchronize automatically, the WSUS server will synchronize at set intervals. Set the time of the First synchronization and specify the number of Synchronizations per day that you want this server to perform. For example, if you specify that there should be four synchronizations per day, starting at 3:00 A.M., synchronizations will occur at 3:00 A.M., 9:00 A.M., 3:00 P.M., and 9:00 P.M. 3. Click OK to save your selections. 4. In the navigation pane of the WSUS Administration Console, select Synchronizations. 5. Right-click or move to the Actions pane on the right side, and then click Synchronize Now. If you do not see the Actions pane on the right side of the console, on the console toolbar click View, click Customize, and ensure that the Action pane check box is selected. 6. After the synchronization is complete, in the left panel, click Updates to view the list of updates.
Next Step
Step 5: Configure Client Updates
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Step 5: Configure Client Updates
In Windows Server Update Services 3.0 (WSUS 3.0 SP2), the WSUS Setup automatically configures IIS to distribute the latest version of Automatic Updates to each client computer that contacts the WSUS server. The best way to configure Automatic Updates depends on the network environment. In an environment that uses Active Directory directory service, you can use an existing domain–based Group Policy object (GPO) or create a new GPO. In an environment without Active Directory, use the Local GPO. In this step, you will configure Automatic Updates and then point the client computers to the WSUS server. The following procedures assume that your network runs Active Directory. These procedures also assume that you are familiar with Group Policy and use it to manage the network.
For more information about Group Policy, refer to the Group Policy Tech Center Web site at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=47375.
19
Step 5 Procedures
In step 4, you completed configuration of the updates that you want to download. Use this set of procedures to configure automatic updates for client computers. 1. Configure Automatic Updates in Group Policy. 2. Point a client computer to the WSUS server. 3. Manually start detection by the WSUS server. Perform the first two procedures on the domain–based GPO of your choice, and the third procedure at a command prompt on the client computer.
1. In the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), browse to the GPO on which you want to configure WSUS, and then click Edit. 2. In the GPMC, expand Computer Configuration, expand Administrative Templates, expand Windows Components, and then click Windows Update. 3. In the details pane, double-click Configure Automatic Updates. 4. Click Enabled, and then click one of the following options: Notify for download and notify for install. This option notifies a logged-on administrative user before the download and before you install the updates. Auto download and notify for install. This option automatically begins downloading updates and then notifies a logged-on administrative user before installing the updates. Auto download and schedule the install. This option automatically begins downloading updates and then installs the updates on the day and time that you specify. Allow local admin to choose setting. This option lets local administrators to use Automatic Updates in Control Panel to select a configuration option. For example, they can choose their own scheduled installation time. Local administrators cannot disable Automatic Updates. 5. Click OK.
1. In the Windows Update details pane, double-click Specify intranet Microsoft update service location.
2. Click Enabled, and type the HTTP URL of the same WSUS server in the Set the intranet update service for detecting updates box and in the Set the intranet statistics server box. For example, type http://servername in both boxes, and then click
To configure Automatic Updates
To point the client computers to the WSUS server
20
OK.
Note If you are using the Local GPO to point the computer to WSUS, this setting takes effect immediately, and this computer appears in the WSUS Administrative Console after a short time. You can speed up this process by manually initiating a detection cycle. After you set up a client computer, it will take several minutes before the computer appears on the Computers page in the WSUS Administration Console. For client computers configured with a domain-based Group Policy, it can take about 20 minutes after Group Policy refreshes (that is, applies any new policy settings to the client computer). By default, Group Policy updates in the background every 90 minutes, with a random offset of 0–30 minutes. If you want to update Group Policy sooner, you can go to a command prompt on the client computer and type gpupdate /force. For client computers configured by using the Local GPO, Group Policy is applied immediately, and the update takes about 20 minutes. If you begin detection manually, you do not have to wait 20 minutes for the client computer to contact WSUS.
1. On the client computer, click Start, and then click Run. 2. Type cmd in the Open box, and then click OK. 3. At the command prompt, type wuauclt.exe /detectnow. This command-line option instructs Automatic Updates to contact the WSUS server immediately.
Next Step
Step 6: Configure Computer Groups
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Step 6: Configure Computer Groups
Computer groups are an important part of Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2) deployments. Computer groups permit you to test updates and target updates to specific computers. There are two default computer groups: All Computers and Unassigned Computers. By default, when each client computer first contacts the WSUS Server, the server adds that client computer to both of these groups.
To manually start detection by the WSUS server
21
You can create as many custom computer groups as you need to manage updates in your organization. As a best practice, create at least one computer group to test updates before you deploy them to other computers in your organization.
Step 6 Procedures
1. Create a test computer group. 2. Move at least one computer into the test group.
1. In the WSUS Administration Console, expand Computers and select All Computers. 2. Right-click All Computers and click Add Computer Group. 3. In the Add Computer Group dialog box, specify the Name of the new test group and click Add.
In the next procedure, you will assign a client computer to the test group. A test computer is any computer that has software and hardware that is consistent with the majority of client computers on the network, yet not assigned to a critical role. After your tests are successful, you can approve the updates for computers in the groups of your choice.
1. In the WSUS Administration Console, click Computers. 2. Click the group of the computer that you want to assign to the test group. 3. In the list of computers, select the computer or computers that you want to assign to the test group. 4. Right-click Change Membership. 5. In the Set Computer Group Membership dialog box, select the test group that you created previously, and then click OK.
Repeat these two procedures, that is, create a group and then assign computer(s) to the group, to create as many additional computer groups as needed to manage updates at your site.
Next Step
Step 7: Approve and Deploy WSUS Updates
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
To create a test group
To assign a computer to the test group
22
Step 7: Approve and Deploy WSUS Updates
In this step, you approve an update for any computers in the test group for Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2). Computers in the group automatically contact the WSUS server over the next 24 hours to obtain the update. You can use the WSUS reporting feature to determine whether those updates were deployed to the test computers. When the tests are successfully completed, you can then approve the updates for the applicable computer groups in your organization.
Step 7 Procedures
Approve and deploy an update. Check the status of an update.
1. On the WSUS Administration Console, click Updates. An update status summary is displayed for All Updates, Critical Updates, Security Updates, and WSUS Updates. 2. In the All Updates section, click Updates needed by computers. 3. On the list of updates, select the updates that you want to approve for installation on your test computer group. Information about a selected update is available in the bottom pane of the Updates panel. To select multiple contiguous updates, hold down the SHIFT key while clicking updates; to select multiple noncontiguous updates, press down the CTRL key while clicking updates. 4. Right-click the selection and click Approve. 5. In the Approve Updates dialog box, select your test group, and then click the down arrow. 6. Click Approved for Install and then click OK. 7. The Approval Progress window appears which shows progress of the tasks that affect update approval. When approval is completed, click Close.
After 24 hours, you can use the WSUS Reports feature to determine whether the updates were deployed to the test group computers.
1. In the navigation pane of the WSUS Administration Console, click Reports. 2. On the Reports page, click the Update Status Summary report. The Updates Report window appears. 3. If you want to filter the list of updates, select the criteria that you want to use, for example, Include updates in these classifications, and then click Run Report on the window's toolbar.
To approve and deploy an update
To check the status of an update
23
4. You will see the Updates Report pane. You can check the status of individual updates by selecting the update in the left section of the pane. The last section of the report pane shows the status summary of the update. 5. You can save or print this report by clicking the applicable icon on the toolbar. 6. After you test the updates, you can approve the updates for installation on the applicable computer groups in your organization.
Additional resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide For more information about how to use WSUS 3.0 SP2, see:
The WSUS Deployment Guide at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139832.
The WSUS Operations Guide at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139838
This guide provides detailed instructions for installing Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2) using either Windows Server Manager or the WSUSSetup.exe file. This guide also contains basic setup instructions for WSUS 3.0 SP2 using either Windows Server Manager or the WSUS Server Configuration Wizard.
Copyright Notice Information in this document, including URL and other Internet Web site references, is subject to change without notice. Unless otherwise noted, the companies, organizations, products, domain names, e-mail addresses, logos, people, places, and events depicted in examples herein are fictitious. No association with any real company, organization, product, domain name, e-mail address, logo, person, place, or event is intended or should be inferred. Complying with all applicable copyright laws is the responsibility of the user. Without limiting the rights under copyright, no part of this document may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise), or for any purpose, without the express written permission of Microsoft Corporation. Microsoft may have patents, patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights covering subject matter in this document. Except as expressly provided in any written license agreement from Microsoft, the furnishing of this document does not give you any license to these patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property. © 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft, Active Directory, ActiveX, Authenticode, Excel, InfoPath, Internet Explorer, MSDN, Outlook, Visual Studio, Win32, Windows, Windows Server, and Windows Vista are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
Contents
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide ................................................... 5
Additional References .............................................................................................................. 5
Step 1: Confirm WSUS 3.0 SP2 Installation Requirements .......................................................... 5
Server Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing WSUS 3.0 SP2 ............................. 6
Client Software Requirements .................................................................................................. 6
Permissions ............................................................................................................................. 6
Preparing to Install WSUS 3.0 SP2 .......................................................................................... 6
Next Step ................................................................................................................................ 7
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................... 7
Step 2: Install WSUS Server or Administration Console ............................................................... 7
If You Are Using Server Manager ............................................................................................. 8
If You Are Using the WSUSSetup.exe File ............................................................................... 8
Using the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Setup Wizard ................................................................................... 8
Next Step ............................................................................................................................... 11
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................. 11
Step 3: Configure the Network Connections............................................................................... 11
Next Step ............................................................................................................................... 14
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................. 15
Step 4: Configure Updates and Synchronization ........................................................................ 15
Step 4 Procedures ................................................................................................................. 15
If You Are Using the Windows Server Update Services Configuration Wizard ......................... 15
If You Are Using the WSUS Administration Console ............................................................... 17
Next Step ............................................................................................................................... 18
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................. 18
Step 5: Configure Client Updates............................................................................................... 18
Step 5 Procedures ................................................................................................................. 19
Next Step ............................................................................................................................... 20
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................. 20
Step 6: Configure Computer Groups .......................................................................................... 20
Step 6 Procedures ................................................................................................................. 21
Next Step ............................................................................................................................... 21
Additional Resources ............................................................................................................. 21
Step 7: Approve and Deploy WSUS Updates............................................................................. 22
Step 7 Procedures ................................................................................................................. 22
Additional resources............................................................................................................... 23
5
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2) provides a comprehensive solution for managing updates to your network. This guide provides instructions for the basic installation and deployment tasks by using WSUS 3.0 SP2 on your network. This guide contains the following sections:
Step 1: Confirm WSUS 3.0 SP2 Installation Requirements
Step 2: Install WSUS Server or Administration Console
Step 3: Configure the Network Connections
Step 4: Configure Updates and Synchronization
Step 5: Configure Client Updates
Step 6: Configure Computer Groups
Step 7: Approve and Deploy WSUS Updates
Additional References
WSUS 3.0 SP2 is a feature-rich update management solution. For complete information about installing and using WSUS, refer to the following Web sites:
The WSUS Deployment Guide at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139832.
The WSUS Operations Guide at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139838.
The WSUS Release Notes at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139840.
Step 1: Confirm WSUS 3.0 SP2 Installation Requirements
Before you install or upgrade to Windows Server Upgrade Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2), confirm that both the server and the client computers meet the WSUS 3.0 SP2 system requirements and confirm that you have the necessary permissions to complete the installation.
6
Server Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing WSUS 3.0 SP2
1. Confirm that the server meets the WSUS 3.0 SP2 system requirements for hardware, operating system, and other required software. System requirements are listed in the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Release Notes at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139840. If you are using Server Manager to install the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Server, you can confirm that you meet the software requirements by following the steps in the “Preparing to Install WSUS 3.0 SP2” section. 2. If you install roles or software updates that require you to restart the server when installation is complete, then restart the server before you install WSUS 3.0 SP2.
Client Software Requirements
Automatic Updates is the client of WSUS 3.0. Automatic Updates has no hardware requirements other than being connected to the network.
1. Confirm that computer on which you are installing Automatic Updates meets the WSUS 3.0 SP2 system requirements for Client computers. System requirements are listed in the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Release Notes at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139840. 2. If you install software updates that require you to restart the computer, restart it before you install WSUS 3.0 SP2.
Permissions
The following permissions are required for the specified users and directories: 1. The NT Authority\Network Service account must have Full Control permission for the following folders so that the WSUS Administration snap-in displays correctly: %windir%\Microsoft .NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\Temporary ASP.NET Files %windir%\Temp 2. Confirm that the account that you plan to use to install WSUS 3.0 SP2 is a member of the Local Administrators group.
Preparing to Install WSUS 3.0 SP2
If you are running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 SP2, you can install WSUS 3.0 SP2 from Server Manager. If you are using another supported operating system, or installing only the WSUS Administration Console, go to the next section of this guide to install WSUS 3.0 SP2 by using the WSUSSetup.exe file.
1. Log on to the server on which you plan to install WSUS 3.0 SP2 by using an account that
To prepare to install the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Server by using Server Manager
7
is a member of the Local Administrators group. 2. Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager. 3. In the right side pane of the Server Manager window, in the Roles Summary section, click Add Roles. 4. If the Before You Begin page appears, click Next. 5. On the Select Server Roles page, confirm that Application Server and Web Server (IIS) are selected. If they have been selected, use the remainder of this step to confirm that the required role services are selected. Otherwise, install Application Server and Web Server (IIS) as follows. a. On the Select Server Roles page, select Application Server and Web Server (IIS). Click Next. b. If you are installing Application Role Services, on the Application Server page, click Next. On the Application Server Role Services page, accept the default settings, and then click Next. c. If you are installing Web Server IIS, on the Web Server (IIS) page, click Next. On the Web Server (IIS) Role Services page, in addition to the default settings, select ASP.NET, Windows Authentication, Dynamic Content Compression, and IIS 6 Management Compatibility. If the Add Roles Wizard window appears, click Add Required Role Services. Click Next. d. On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install. e. On the Installation Results page, confirm that an “Installation succeeded” message appears for the role services that you installed in this step, and then click Close.
Next Step
Step 2: Install WSUS Server or Administration Console
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Step 2: Install WSUS Server or Administration Console
After you make sure that the server meets the minimum system requirements and that the necessary account permissions were granted, you are ready to install Windows Server Upgrade Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2). Start the installation of WSUS 3.0 SP2 by using the applicable procedure for your operating system and kind of installation (by using either Server Manager or the WSUSSetup.exe file).
8
If You Are Using Server Manager
1. Log on to the server on which you plan to install WSUS 3.0 SP2 by using an account that is a member of the local Administrators group. 2. Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager. 3. In the right side pane of the Server Manager window, in the Roles Summary section, click Add Roles. 4. If the Before You Begin page appears, click Next. 5. On the Select Server Roles page, select Windows Server Update Services. 6. On the Windows Server Update Services page, click Next. 7. On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install. 8. When the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Setup Wizard is started, skip the next section and see the “To continue installing WSUS 3.0 SP2” procedure.
If You Are Using the WSUSSetup.exe File
1. Log on to the server on which you plan to install WSUS 3.0 SP2 by using an account that is a member of the Local Administrators group. 2. Double-click the WSUSSetup.exe installer file. 3. When the Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Setup Wizard is started, see the “To continue installing WSUS 3.0 SP2” procedure.
Using the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Setup Wizard
The WSUS Setup Wizard is launched from Server Manager or from the WSUSSetup.exe file.
1. On the Welcome page of the Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Setup Wizard, click Next. 2. On the Installation Mode Selection page, select Full server installation including Administration Console if you want to install the WSUS server on this computer, or Administration Console only if you want to install the administration console only. 3. On the License Agreement page, read the terms of the license agreement, click I accept the terms of the License agreement, and then click Next.
4. You can specify where clients get updates on the Select Update Source page of the
To start the installation of WSUS 3.0 SP2 Server by using Server Manager
To start the installation of WSUS 3.0 SP2 Server or the WSUS 3.0 SP2 Administration Console by using the WSUSSetup.exe file
To continue installing WSUS 3.0 SP2
9
installation wizard. By default, the Store updates locally check box is selected and updates will be stored on the WSUS server in the location that you specify. If you clear the Store updates locally check box, client computers obtain approved updates by connecting to Microsoft Update. Make your selection, and then click Next.
5. On the Database Options page, select the software that is used to manage the WSUS 3.0 database. By default, the installation wizard offers to install Windows Internal Database. If you do not want to use Windows Internal Database, provide an instance of Microsoft SQL Server for WSUS to use by selecting Use an existing database on this server or Use an existing database server on a remote computer. Type the instance name in the applicable box. The instance name should appear as
10
6. If you have opted to connect to a SQL Server, on the Connecting to SQL Server Instance page, WSUS will try to connect to the specified instance of SQL Server. When it has connected successfully, click Next to continue. 7. On the Web Site Selection page, specify the Web site that WSUS will use. If you want to use the default Web site on port 80, select Use the existing IIS Default Web site. If you already have a Web site on port 80, you can create an alternate site on port 8530 or 8531 by selecting Create a Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Web site. Click Next.
11
8. On the Ready to Install Windows Server Update Services page, review the selections, and then click Next. 9. The final page of the installation wizard will let you know if the WSUS installation completed successfully. After you click Finish the configuration wizard will start.
Next Step
Step 3: Configure the Network Connections
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Step 3: Configure the Network Connections
After you install Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2), the configuration wizard will launch automatically. You can also run the wizard later through the Options page of the WSUS Administration Console.
12
Before you start the configuration process, be sure that you know the answers to the following questions: 1. Is the server's firewall configured to allow clients to access the server? 2. Can this computer connect to the upstream server (such as Microsoft Update)? 3. Do you have the name of the proxy server and the user credentials for the proxy server, if you need them? By default, WSUS 3.0 SP2 is configured to use Microsoft Update as the location from which to obtain updates. If you have a proxy server on the network, you can configure WSUS 3.0 SP2 to use the proxy server. If there is a corporate firewall between WSUS and the Internet, you might have to configure the firewall to ensure that WSUS can obtain updates.
Note Although Internet connectivity is required to download updates from Microsoft Update, WSUS offers you the ability to import updates onto networks that are not connected to the Internet. Step 3 contains the following procedures: Configure your firewall. Specify the way this server will obtain updates (either from Microsoft Update or from another WSUS server). Configure proxy server settings, so that WSUS can obtain updates.
If there is a corporate firewall between WSUS and the Internet, you might have to configure that firewall to ensure WSUS can obtain updates. To obtain updates from Microsoft Update, the WSUS server uses port 80 for HTTP protocol and port 443 for HTTPS protocol. This is not configurable. If your organization does not enable port 80 or port 443 to be open to all addresses, you can restrict access to only the following domains, so that WSUS and Automatic Updates can communicate with Microsoft Update: http://windowsupdate.microsoft.com http://*.windowsupdate.microsoft.com https://*.windowsupdate.microsoft.com http://*.update.microsoft.com https://*.update.microsoft.com http://*.windowsupdate.com http://download.windowsupdate.com http://download.microsoft.com http://*.download.windowsupdate.com http://wustat.windows.com
To configure your firewall
13
http://ntservicepack.microsoft.com
Note These instructions about how to configure the firewall are meant for a corporate firewall positioned between WSUS and the Internet. Because WSUS initiates all of its network traffic, you do not have to configure Windows Firewall on the WSUS server. Although the connection between Microsoft Update and WSUS requires ports 80 and 443 to be open, you can configure multiple WSUS servers to synchronize with a custom port. The next two procedures assume that you are using the Configuration Wizard. In a later section in this step, you will learn how to start the WSUS Administration snap-in and configure the server through the Options page.
1. From the configuration wizard, after joining the Microsoft Improvement Program, click Next to select the upstream server. 2. If you choose to synchronize from Microsoft Update, you are finished with the Options page. Click Next, or select Specify Proxy Server from the navigation pane. 3. If you choose to synchronize from another WSUS server, specify the server name and the port on which this server will communicate with the upstream server. 4. To use SSL, select the Use SSL when synchronizing update information check box. In that case the servers will use port 443 for synchronization. (Make sure that both this server and the upstream server support SSL.) 5. If this is a replica server, select the This is a replica of the upstream server check box. 6. At this point, you are finished with upstream server configuration. Click Next, or select Specify proxy server from the left navigation pane.
1. On the Specify Proxy Server page of the configuration wizard, select the Use a proxy server when synchronizing check box, and then type the proxy server name and port number (port 80 by default) in the corresponding boxes. 2. If you want to connect to the proxy server by using specific user credentials, select the Use user credentials to connect to the proxy server check box, and then type the user name, domain, and password of the user in the corresponding boxes. If you want to enable basic authentication for the user connecting to the proxy server, select the Allow basic authentication (password is sent in cleartext) check box. 3. At this point, you are finished with proxy server configuration. Click Next to go to the next page, where you can start to set up the synchronization process.
The following two procedures assume that you are using the WSUS Administration snap-in for configuration. These two procedures show how to start the WSUS Administration snap-in and configure the server from the Options page.
To specify the way this server will obtain updates
To configure proxy server settings
14
To start the WSUS Administration Console, click Start, point to All Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Windows Server Update Services 3.0.
Note In order to use all the features of the console, log on as a member of either the WSUS Administrators or the Local Administrators security groups on the server on which WSUS is installed. Members of the WSUS Reporters security group have read-only access to the console.
1. On the WSUS console, click Options in the left pane under the name of this server, and then click Update Source and Proxy Server in the middle pane. A dialog box will be displayed with Update Source and Proxy Server tabs. 2. In the Update Source tab, select the location from which this server will obtain updates. If you choose to synchronize from Microsoft Update (the default), you are finished with this wizard page. 3. If you choose to synchronize from another WSUS server, you have to specify the port on which the servers will communicate (the default is port 80). If you select a different port, you should ensure that both servers can use that port. 4. You may also specify whether to use SSL when synchronizing from the upstream WSUS server. In that case, the servers will use port 443 to synchronize from the upstream server. 5. If this server is a replica of the second WSUS server, select the This is a replica of the upstream server check box. In this case all updates must be approved on the upstream WSUS server only. 6. In the Proxy server tab, select the Use a proxy server when synchronizing check box, and then type the proxy server name and port number (port 80 by default) in the corresponding boxes. 7. If you want to connect to the proxy server by using specific user credentials, select the Use user credentials to connect to the proxy server check box, and then type the user name, domain, and password of the user in the corresponding boxes. If you want to enable basic authentication for the user connecting to the proxy server, select the Allow basic authentication (password in cleartext) check box. 8. Click OK to save these settings.
Next Step
Step 4: Configure Updates and Synchronization
To start the WSUS Administration Console
To specify an update source and proxy server
15
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Step 4: Configure Updates and Synchronization
This section describes how to configure a set of updates that you want to download by using Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2).
Step 4 Procedures
You can do these procedures by using either the WSUS Configuration Wizard or the WSUS Administration Console. 1. Save and download information about your upstream server and proxy server. 2. Choose the language of the updates. 3. Select the products for which you want to receive updates. 4. Choose the classifications of updates. 5. Specify the synchronization schedule for this server. After you configure the network connection, you can download updates by synchronizing the WSUS server. Synchronization begins when the WSUS server contacts Microsoft Update. After the WSUS makes contact, WSUS determines whether any new updates have been made available since the last time you synchronized. When you synchronize the WSUS server for the first time, all the updates are available and are ready for your approval for installation. The initial synchronization may take a long time. The procedures in this section describe synchronizing with the default settings. WSUS 3.0 SP2 also includes options that enable you to minimize bandwidth use during synchronization.
If You Are Using the Windows Server Update Services Configuration Wizard
In the step 3 procedures, you completed configuration of the upstream server and the proxy server. This next set of procedures starts on the Connect to Upstream Server page of that configuration wizard.
1. On the Connect to Upstream Server page of the configuration wizard, click the Start Connecting button. This both saves and uploads your settings and collects information about available updates.
To save and download your upstream server and proxy information
16
2. While the connection is being made, the Stop Connecting button will be available. If there are problems with the connection, click Stop Connecting, fix the problems, and restart the connection. 3. After the download has completed successfully, click Next.
1. The Choose Languages page lets you receive updates from all languages or from a subset of languages. Selecting a subset of languages will save disk space, but it is important to choose all of the languages that will be needed by all the clients of this WSUS server. If you choose to get updates only for specific languages, select Download updates only in these languages, and select the languages for which you want updates. 2. Click Next.
1. The Choose Products page lets you specify the products for which you want updates. Select product categories, such as Windows, or specific products, such as Windows Server 2008. Selecting a product category will cause all the products in that category to be selected. 2. Click Next.
1. The Choose Classifications page allows you to specify the update classifications you want to obtain. Choose all the classifications or a subset of them. 2. Click Next
1. On the Set Sync Schedule page, you choose whether to perform synchronization manually or automatically. If you choose Synchronize manually, you must start the synchronization process from the WSUS Administration Console. If you choose Synchronize automatically, the WSUS server will synchronize at set intervals. Set the time of the First synchronization and specify the number of Synchronizations per day that you want this server to perform. For example, if you specify that there should be four synchronizations per day, starting at 3:00 A.M., synchronizations will occur at 3:00 A.M., 9:00 A.M., 3:00 P.M., and 9:00 P.M. 2. Click Next.
3. On the Finished page, you can start the WSUS Administration Console by leaving the Launch the Windows Server Update Services Administrations snap-in check box
To choose update languages
To choose update products
To choose update classifications
To configure the synchronization schedule
17
selected, and you can start the first synchronization by leaving the Begin initial synchronization check box selected. 4. Click Finish.
Important You cannot save configuration changes that are made while the server is synchronizing. Wait until synchronization is finished and then make your changes.
If You Are Using the WSUS Administration Console
The following procedures explain how to perform the configuration steps by using the WSUS Administration Console.
1. In the Options panel, click Products and Classifications. A dialog box appears with Products and Classifications tabs. 2. In the Products tab, select the product category or specific products for which you want this server to receive updates, or else select All Products. 3. In the Classifications tab, select the update classifications you want, or else select All Classifications. 4. Click OK to save your selections.
1. In the Options panel, click Update Files and Languages. A dialog box appears with Update Files and Update Languages tabs. 2. In the Update Files tab, choose whether to Store update files locally on this server or to have all client computers install from Microsoft Update. If you decide to store update files on this server, you also decide whether to download only those updates that are approved or to download express installation files. 3. In the Update Languages tab, if you are storing update files locally, you choose to Download updates for all languages (the default), or to Download updates only in the specified languages. If this WSUS server has downstream servers, they will receive updates only in the languages specified by the upstream server. 4. Click OK to save these settings.
1. In the Options panel, click Synchronization Schedule.
2. In the Synchronization Schedule tab, you choose whether to perform synchronization
To choose products and update classifications
To choose update files and languages
To synchronize the WSUS server
18
manually or automatically. If you choose Synchronize manually, you will have to start the synchronization process from the WSUS Administration Console. If you choose Synchronize automatically, the WSUS server will synchronize at set intervals. Set the time of the First synchronization and specify the number of Synchronizations per day that you want this server to perform. For example, if you specify that there should be four synchronizations per day, starting at 3:00 A.M., synchronizations will occur at 3:00 A.M., 9:00 A.M., 3:00 P.M., and 9:00 P.M. 3. Click OK to save your selections. 4. In the navigation pane of the WSUS Administration Console, select Synchronizations. 5. Right-click or move to the Actions pane on the right side, and then click Synchronize Now. If you do not see the Actions pane on the right side of the console, on the console toolbar click View, click Customize, and ensure that the Action pane check box is selected. 6. After the synchronization is complete, in the left panel, click Updates to view the list of updates.
Next Step
Step 5: Configure Client Updates
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Step 5: Configure Client Updates
In Windows Server Update Services 3.0 (WSUS 3.0 SP2), the WSUS Setup automatically configures IIS to distribute the latest version of Automatic Updates to each client computer that contacts the WSUS server. The best way to configure Automatic Updates depends on the network environment. In an environment that uses Active Directory directory service, you can use an existing domain–based Group Policy object (GPO) or create a new GPO. In an environment without Active Directory, use the Local GPO. In this step, you will configure Automatic Updates and then point the client computers to the WSUS server. The following procedures assume that your network runs Active Directory. These procedures also assume that you are familiar with Group Policy and use it to manage the network.
For more information about Group Policy, refer to the Group Policy Tech Center Web site at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=47375.
19
Step 5 Procedures
In step 4, you completed configuration of the updates that you want to download. Use this set of procedures to configure automatic updates for client computers. 1. Configure Automatic Updates in Group Policy. 2. Point a client computer to the WSUS server. 3. Manually start detection by the WSUS server. Perform the first two procedures on the domain–based GPO of your choice, and the third procedure at a command prompt on the client computer.
1. In the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), browse to the GPO on which you want to configure WSUS, and then click Edit. 2. In the GPMC, expand Computer Configuration, expand Administrative Templates, expand Windows Components, and then click Windows Update. 3. In the details pane, double-click Configure Automatic Updates. 4. Click Enabled, and then click one of the following options: Notify for download and notify for install. This option notifies a logged-on administrative user before the download and before you install the updates. Auto download and notify for install. This option automatically begins downloading updates and then notifies a logged-on administrative user before installing the updates. Auto download and schedule the install. This option automatically begins downloading updates and then installs the updates on the day and time that you specify. Allow local admin to choose setting. This option lets local administrators to use Automatic Updates in Control Panel to select a configuration option. For example, they can choose their own scheduled installation time. Local administrators cannot disable Automatic Updates. 5. Click OK.
1. In the Windows Update details pane, double-click Specify intranet Microsoft update service location.
2. Click Enabled, and type the HTTP URL of the same WSUS server in the Set the intranet update service for detecting updates box and in the Set the intranet statistics server box. For example, type http://servername in both boxes, and then click
To configure Automatic Updates
To point the client computers to the WSUS server
20
OK.
Note If you are using the Local GPO to point the computer to WSUS, this setting takes effect immediately, and this computer appears in the WSUS Administrative Console after a short time. You can speed up this process by manually initiating a detection cycle. After you set up a client computer, it will take several minutes before the computer appears on the Computers page in the WSUS Administration Console. For client computers configured with a domain-based Group Policy, it can take about 20 minutes after Group Policy refreshes (that is, applies any new policy settings to the client computer). By default, Group Policy updates in the background every 90 minutes, with a random offset of 0–30 minutes. If you want to update Group Policy sooner, you can go to a command prompt on the client computer and type gpupdate /force. For client computers configured by using the Local GPO, Group Policy is applied immediately, and the update takes about 20 minutes. If you begin detection manually, you do not have to wait 20 minutes for the client computer to contact WSUS.
1. On the client computer, click Start, and then click Run. 2. Type cmd in the Open box, and then click OK. 3. At the command prompt, type wuauclt.exe /detectnow. This command-line option instructs Automatic Updates to contact the WSUS server immediately.
Next Step
Step 6: Configure Computer Groups
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
Step 6: Configure Computer Groups
Computer groups are an important part of Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2) deployments. Computer groups permit you to test updates and target updates to specific computers. There are two default computer groups: All Computers and Unassigned Computers. By default, when each client computer first contacts the WSUS Server, the server adds that client computer to both of these groups.
To manually start detection by the WSUS server
21
You can create as many custom computer groups as you need to manage updates in your organization. As a best practice, create at least one computer group to test updates before you deploy them to other computers in your organization.
Step 6 Procedures
1. Create a test computer group. 2. Move at least one computer into the test group.
1. In the WSUS Administration Console, expand Computers and select All Computers. 2. Right-click All Computers and click Add Computer Group. 3. In the Add Computer Group dialog box, specify the Name of the new test group and click Add.
In the next procedure, you will assign a client computer to the test group. A test computer is any computer that has software and hardware that is consistent with the majority of client computers on the network, yet not assigned to a critical role. After your tests are successful, you can approve the updates for computers in the groups of your choice.
1. In the WSUS Administration Console, click Computers. 2. Click the group of the computer that you want to assign to the test group. 3. In the list of computers, select the computer or computers that you want to assign to the test group. 4. Right-click Change Membership. 5. In the Set Computer Group Membership dialog box, select the test group that you created previously, and then click OK.
Repeat these two procedures, that is, create a group and then assign computer(s) to the group, to create as many additional computer groups as needed to manage updates at your site.
Next Step
Step 7: Approve and Deploy WSUS Updates
Additional Resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide
To create a test group
To assign a computer to the test group
22
Step 7: Approve and Deploy WSUS Updates
In this step, you approve an update for any computers in the test group for Windows Server Update Services 3.0 Service Pack 2 (WSUS 3.0 SP2). Computers in the group automatically contact the WSUS server over the next 24 hours to obtain the update. You can use the WSUS reporting feature to determine whether those updates were deployed to the test computers. When the tests are successfully completed, you can then approve the updates for the applicable computer groups in your organization.
Step 7 Procedures
Approve and deploy an update. Check the status of an update.
1. On the WSUS Administration Console, click Updates. An update status summary is displayed for All Updates, Critical Updates, Security Updates, and WSUS Updates. 2. In the All Updates section, click Updates needed by computers. 3. On the list of updates, select the updates that you want to approve for installation on your test computer group. Information about a selected update is available in the bottom pane of the Updates panel. To select multiple contiguous updates, hold down the SHIFT key while clicking updates; to select multiple noncontiguous updates, press down the CTRL key while clicking updates. 4. Right-click the selection and click Approve. 5. In the Approve Updates dialog box, select your test group, and then click the down arrow. 6. Click Approved for Install and then click OK. 7. The Approval Progress window appears which shows progress of the tasks that affect update approval. When approval is completed, click Close.
After 24 hours, you can use the WSUS Reports feature to determine whether the updates were deployed to the test group computers.
1. In the navigation pane of the WSUS Administration Console, click Reports. 2. On the Reports page, click the Update Status Summary report. The Updates Report window appears. 3. If you want to filter the list of updates, select the criteria that you want to use, for example, Include updates in these classifications, and then click Run Report on the window's toolbar.
To approve and deploy an update
To check the status of an update
23
4. You will see the Updates Report pane. You can check the status of individual updates by selecting the update in the left section of the pane. The last section of the report pane shows the status summary of the update. 5. You can save or print this report by clicking the applicable icon on the toolbar. 6. After you test the updates, you can approve the updates for installation on the applicable computer groups in your organization.
Additional resources
Windows Server Update Services 3.0 SP2 Step By Step Guide For more information about how to use WSUS 3.0 SP2, see:
The WSUS Deployment Guide at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139832.
The WSUS Operations Guide at http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=139838
To Access….Run Command
To Access….Run Command
Accessibility Controls access.cpl
Add Hardware Wizard hdwwiz.cpl
Add/Remove Programs appwiz.cpl
Administrative Tools control admintools
Automatic Updates wuaucpl.cpl
Bluetooth Transfer Wizard fsquirt
Calculator calc
Certificate Manager certmgr.msc
Character Map charmap
Check Disk Utility chkdsk
Clipboard Viewer clipbrd
Command Prompt cmd
Component Services dcomcnfg
Computer Management compmgmt.msc
Date and Time Properties timedate.cpl
DDE Shares ddeshare
Device Manager devmgmt.msc
Direct X Control Panel (If Installed)* directx.cpl
Direct X Troubleshooter dxdiag
Disk Cleanup Utility cleanmgr
Disk Defragment dfrg.msc
Disk Management diskmgmt.msc
Disk Partition Manager diskpart
Display Properties control desktop
Display Properties desk.cpl
Display Properties (w/Appearance Tab Preselected) control color
Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility drwtsn32
Driver Verifier Utility verifier
Event Viewer eventvwr.msc
File Signature Verification Tool sigverif
Findfast findfast.cpl
Folders Properties control folders
Fonts control fonts
Fonts Folder fonts
Free Cell Card Game freecell
Game Controllers joy.cpl
Group Policy Editor (XP Prof) gpedit.msc
Hearts Card Game mshearts
Iexpress Wizard iexpress
Indexing Service ciadv.msc
Internet Properties inetcpl.cpl
IP Configuration (Display Connection Configuration) ipconfig /all
IP Configuration (Display DNS Cache Contents) ipconfig /displaydns
IP Configuration (Delete DNS Cache Contents) ipconfig /flushdns
IP Configuration (Release All Connections) ipconfig /release
IP Configuration (Renew All Connections) ipconfig /renew
IP Configuration (Refreshes DHCP & Re-Registers DNS) ipconfig /registerdns
IP Configuration (Display DHCP Class ID) ipconfig /showclassid
IP Configuration (Modifies DHCP Class ID) ipconfig /setclassid
Java Control Panel (If Installed) jpicpl32.cpl
Java Control Panel (If Installed) javaws
Keyboard Properties control keyboard
Local Security Settings secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups lusrmgr.msc
Logs You Out Of Windows logoff
Microsoft Chat winchat
Minesweeper Game winmine
Mouse Properties control mouse
Mouse Properties main.cpl
Network Connections control netconnections
Network Connections ncpa.cpl
Network Setup Wizard netsetup.cpl
Notepad notepad
Nview Desktop Manager (If Installed) nvtuicpl.cpl
Object Packager packager
ODBC Data Source Administrator odbccp32.cpl
On Screen Keyboard osk
Opens AC3 Filter (If Installed) ac3filter.cpl
Password Properties password.cpl
Performance Monitor perfmon.msc
Performance Monitor perfmon
Phone and Modem Options telephon.cpl
Power Configuration powercfg.cpl
Printers and Faxes control printers
Printers Folder printers
Private Character Editor eudcedit
Quicktime (If Installed) QuickTime.cpl
Regional Settings intl.cpl
Registry Editor regedit
Registry Editor regedit32
Remote Desktop mstsc
Removable Storage ntmsmgr.msc
Removable Storage Operator Requests ntmsoprq.msc
Resultant Set of Policy (XP Prof) rsop.msc
Scanners and Cameras sticpl.cpl
Scheduled Tasks control schedtasks
Security Center wscui.cpl
Services services.msc
Shared Folders fsmgmt.msc
Shuts Down Windows shutdown
Sounds and Audio mmsys.cpl
Spider Solitare Card Game spider
SQL Client Configuration cliconfg
System Configuration Editor sysedit
System Configuration Utility msconfig
System File Checker Utility (Scan Immediately) sfc /scannow
System File Checker Utility (Scan Once At Next Boot) sfc /scanonce
System File Checker Utility (Scan On Every Boot) sfc /scanboot
System File Checker Utility (Return to Default Setting) sfc /revert
System File Checker Utility (Purge File Cache) sfc /purgecache
System File Checker Utility (Set Cache Size to size x) sfc /cachesize=x
System Properties sysdm.cpl
Task Manager taskmgr
Telnet Client telnet
User Account Management nusrmgr.cpl
Utility Manager utilman
Windows Firewall firewall.cpl
Windows Magnifier magnify
Windows Management Infrastructure wmimgmt.msc
Windows System Security Tool syskey
Windows Update Launches wupdmgr
Windows XP Tour Wizard tourstart
Wordpad write
Accessibility Controls access.cpl
Add Hardware Wizard hdwwiz.cpl
Add/Remove Programs appwiz.cpl
Administrative Tools control admintools
Automatic Updates wuaucpl.cpl
Bluetooth Transfer Wizard fsquirt
Calculator calc
Certificate Manager certmgr.msc
Character Map charmap
Check Disk Utility chkdsk
Clipboard Viewer clipbrd
Command Prompt cmd
Component Services dcomcnfg
Computer Management compmgmt.msc
Date and Time Properties timedate.cpl
DDE Shares ddeshare
Device Manager devmgmt.msc
Direct X Control Panel (If Installed)* directx.cpl
Direct X Troubleshooter dxdiag
Disk Cleanup Utility cleanmgr
Disk Defragment dfrg.msc
Disk Management diskmgmt.msc
Disk Partition Manager diskpart
Display Properties control desktop
Display Properties desk.cpl
Display Properties (w/Appearance Tab Preselected) control color
Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility drwtsn32
Driver Verifier Utility verifier
Event Viewer eventvwr.msc
File Signature Verification Tool sigverif
Findfast findfast.cpl
Folders Properties control folders
Fonts control fonts
Fonts Folder fonts
Free Cell Card Game freecell
Game Controllers joy.cpl
Group Policy Editor (XP Prof) gpedit.msc
Hearts Card Game mshearts
Iexpress Wizard iexpress
Indexing Service ciadv.msc
Internet Properties inetcpl.cpl
IP Configuration (Display Connection Configuration) ipconfig /all
IP Configuration (Display DNS Cache Contents) ipconfig /displaydns
IP Configuration (Delete DNS Cache Contents) ipconfig /flushdns
IP Configuration (Release All Connections) ipconfig /release
IP Configuration (Renew All Connections) ipconfig /renew
IP Configuration (Refreshes DHCP & Re-Registers DNS) ipconfig /registerdns
IP Configuration (Display DHCP Class ID) ipconfig /showclassid
IP Configuration (Modifies DHCP Class ID) ipconfig /setclassid
Java Control Panel (If Installed) jpicpl32.cpl
Java Control Panel (If Installed) javaws
Keyboard Properties control keyboard
Local Security Settings secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups lusrmgr.msc
Logs You Out Of Windows logoff
Microsoft Chat winchat
Minesweeper Game winmine
Mouse Properties control mouse
Mouse Properties main.cpl
Network Connections control netconnections
Network Connections ncpa.cpl
Network Setup Wizard netsetup.cpl
Notepad notepad
Nview Desktop Manager (If Installed) nvtuicpl.cpl
Object Packager packager
ODBC Data Source Administrator odbccp32.cpl
On Screen Keyboard osk
Opens AC3 Filter (If Installed) ac3filter.cpl
Password Properties password.cpl
Performance Monitor perfmon.msc
Performance Monitor perfmon
Phone and Modem Options telephon.cpl
Power Configuration powercfg.cpl
Printers and Faxes control printers
Printers Folder printers
Private Character Editor eudcedit
Quicktime (If Installed) QuickTime.cpl
Regional Settings intl.cpl
Registry Editor regedit
Registry Editor regedit32
Remote Desktop mstsc
Removable Storage ntmsmgr.msc
Removable Storage Operator Requests ntmsoprq.msc
Resultant Set of Policy (XP Prof) rsop.msc
Scanners and Cameras sticpl.cpl
Scheduled Tasks control schedtasks
Security Center wscui.cpl
Services services.msc
Shared Folders fsmgmt.msc
Shuts Down Windows shutdown
Sounds and Audio mmsys.cpl
Spider Solitare Card Game spider
SQL Client Configuration cliconfg
System Configuration Editor sysedit
System Configuration Utility msconfig
System File Checker Utility (Scan Immediately) sfc /scannow
System File Checker Utility (Scan Once At Next Boot) sfc /scanonce
System File Checker Utility (Scan On Every Boot) sfc /scanboot
System File Checker Utility (Return to Default Setting) sfc /revert
System File Checker Utility (Purge File Cache) sfc /purgecache
System File Checker Utility (Set Cache Size to size x) sfc /cachesize=x
System Properties sysdm.cpl
Task Manager taskmgr
Telnet Client telnet
User Account Management nusrmgr.cpl
Utility Manager utilman
Windows Firewall firewall.cpl
Windows Magnifier magnify
Windows Management Infrastructure wmimgmt.msc
Windows System Security Tool syskey
Windows Update Launches wupdmgr
Windows XP Tour Wizard tourstart
Wordpad write
To Access….Run Command
To Access….Run Command
Accessibility Controls access.cpl
Add Hardware Wizard hdwwiz.cpl
Add/Remove Programs appwiz.cpl
Administrative Tools control admintools
Automatic Updates wuaucpl.cpl
Bluetooth Transfer Wizard fsquirt
Calculator calc
Certificate Manager certmgr.msc
Character Map charmap
Check Disk Utility chkdsk
Clipboard Viewer clipbrd
Command Prompt cmd
Component Services dcomcnfg
Computer Management compmgmt.msc
Date and Time Properties timedate.cpl
DDE Shares ddeshare
Device Manager devmgmt.msc
Direct X Control Panel (If Installed)* directx.cpl
Direct X Troubleshooter dxdiag
Disk Cleanup Utility cleanmgr
Disk Defragment dfrg.msc
Disk Management diskmgmt.msc
Disk Partition Manager diskpart
Display Properties control desktop
Display Properties desk.cpl
Display Properties (w/Appearance Tab Preselected) control color
Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility drwtsn32
Driver Verifier Utility verifier
Event Viewer eventvwr.msc
File Signature Verification Tool sigverif
Findfast findfast.cpl
Folders Properties control folders
Fonts control fonts
Fonts Folder fonts
Free Cell Card Game freecell
Game Controllers joy.cpl
Group Policy Editor (XP Prof) gpedit.msc
Hearts Card Game mshearts
Iexpress Wizard iexpress
Indexing Service ciadv.msc
Internet Properties inetcpl.cpl
IP Configuration (Display Connection Configuration) ipconfig /all
IP Configuration (Display DNS Cache Contents) ipconfig /displaydns
IP Configuration (Delete DNS Cache Contents) ipconfig /flushdns
IP Configuration (Release All Connections) ipconfig /release
IP Configuration (Renew All Connections) ipconfig /renew
IP Configuration (Refreshes DHCP & Re-Registers DNS) ipconfig /registerdns
IP Configuration (Display DHCP Class ID) ipconfig /showclassid
IP Configuration (Modifies DHCP Class ID) ipconfig /setclassid
Java Control Panel (If Installed) jpicpl32.cpl
Java Control Panel (If Installed) javaws
Keyboard Properties control keyboard
Local Security Settings secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups lusrmgr.msc
Logs You Out Of Windows logoff
Microsoft Chat winchat
Minesweeper Game winmine
Mouse Properties control mouse
Mouse Properties main.cpl
Network Connections control netconnections
Network Connections ncpa.cpl
Network Setup Wizard netsetup.cpl
Notepad notepad
Nview Desktop Manager (If Installed) nvtuicpl.cpl
Object Packager packager
ODBC Data Source Administrator odbccp32.cpl
On Screen Keyboard osk
Opens AC3 Filter (If Installed) ac3filter.cpl
Password Properties password.cpl
Performance Monitor perfmon.msc
Performance Monitor perfmon
Phone and Modem Options telephon.cpl
Power Configuration powercfg.cpl
Printers and Faxes control printers
Printers Folder printers
Private Character Editor eudcedit
Quicktime (If Installed) QuickTime.cpl
Regional Settings intl.cpl
Registry Editor regedit
Registry Editor regedit32
Remote Desktop mstsc
Removable Storage ntmsmgr.msc
Removable Storage Operator Requests ntmsoprq.msc
Resultant Set of Policy (XP Prof) rsop.msc
Scanners and Cameras sticpl.cpl
Scheduled Tasks control schedtasks
Security Center wscui.cpl
Services services.msc
Shared Folders fsmgmt.msc
Shuts Down Windows shutdown
Sounds and Audio mmsys.cpl
Spider Solitare Card Game spider
SQL Client Configuration cliconfg
System Configuration Editor sysedit
System Configuration Utility msconfig
System File Checker Utility (Scan Immediately) sfc /scannow
System File Checker Utility (Scan Once At Next Boot) sfc /scanonce
System File Checker Utility (Scan On Every Boot) sfc /scanboot
System File Checker Utility (Return to Default Setting) sfc /revert
System File Checker Utility (Purge File Cache) sfc /purgecache
System File Checker Utility (Set Cache Size to size x) sfc /cachesize=x
System Properties sysdm.cpl
Task Manager taskmgr
Telnet Client telnet
User Account Management nusrmgr.cpl
Utility Manager utilman
Windows Firewall firewall.cpl
Windows Magnifier magnify
Windows Management Infrastructure wmimgmt.msc
Windows System Security Tool syskey
Windows Update Launches wupdmgr
Windows XP Tour Wizard tourstart
Wordpad write
Accessibility Controls access.cpl
Add Hardware Wizard hdwwiz.cpl
Add/Remove Programs appwiz.cpl
Administrative Tools control admintools
Automatic Updates wuaucpl.cpl
Bluetooth Transfer Wizard fsquirt
Calculator calc
Certificate Manager certmgr.msc
Character Map charmap
Check Disk Utility chkdsk
Clipboard Viewer clipbrd
Command Prompt cmd
Component Services dcomcnfg
Computer Management compmgmt.msc
Date and Time Properties timedate.cpl
DDE Shares ddeshare
Device Manager devmgmt.msc
Direct X Control Panel (If Installed)* directx.cpl
Direct X Troubleshooter dxdiag
Disk Cleanup Utility cleanmgr
Disk Defragment dfrg.msc
Disk Management diskmgmt.msc
Disk Partition Manager diskpart
Display Properties control desktop
Display Properties desk.cpl
Display Properties (w/Appearance Tab Preselected) control color
Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility drwtsn32
Driver Verifier Utility verifier
Event Viewer eventvwr.msc
File Signature Verification Tool sigverif
Findfast findfast.cpl
Folders Properties control folders
Fonts control fonts
Fonts Folder fonts
Free Cell Card Game freecell
Game Controllers joy.cpl
Group Policy Editor (XP Prof) gpedit.msc
Hearts Card Game mshearts
Iexpress Wizard iexpress
Indexing Service ciadv.msc
Internet Properties inetcpl.cpl
IP Configuration (Display Connection Configuration) ipconfig /all
IP Configuration (Display DNS Cache Contents) ipconfig /displaydns
IP Configuration (Delete DNS Cache Contents) ipconfig /flushdns
IP Configuration (Release All Connections) ipconfig /release
IP Configuration (Renew All Connections) ipconfig /renew
IP Configuration (Refreshes DHCP & Re-Registers DNS) ipconfig /registerdns
IP Configuration (Display DHCP Class ID) ipconfig /showclassid
IP Configuration (Modifies DHCP Class ID) ipconfig /setclassid
Java Control Panel (If Installed) jpicpl32.cpl
Java Control Panel (If Installed) javaws
Keyboard Properties control keyboard
Local Security Settings secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups lusrmgr.msc
Logs You Out Of Windows logoff
Microsoft Chat winchat
Minesweeper Game winmine
Mouse Properties control mouse
Mouse Properties main.cpl
Network Connections control netconnections
Network Connections ncpa.cpl
Network Setup Wizard netsetup.cpl
Notepad notepad
Nview Desktop Manager (If Installed) nvtuicpl.cpl
Object Packager packager
ODBC Data Source Administrator odbccp32.cpl
On Screen Keyboard osk
Opens AC3 Filter (If Installed) ac3filter.cpl
Password Properties password.cpl
Performance Monitor perfmon.msc
Performance Monitor perfmon
Phone and Modem Options telephon.cpl
Power Configuration powercfg.cpl
Printers and Faxes control printers
Printers Folder printers
Private Character Editor eudcedit
Quicktime (If Installed) QuickTime.cpl
Regional Settings intl.cpl
Registry Editor regedit
Registry Editor regedit32
Remote Desktop mstsc
Removable Storage ntmsmgr.msc
Removable Storage Operator Requests ntmsoprq.msc
Resultant Set of Policy (XP Prof) rsop.msc
Scanners and Cameras sticpl.cpl
Scheduled Tasks control schedtasks
Security Center wscui.cpl
Services services.msc
Shared Folders fsmgmt.msc
Shuts Down Windows shutdown
Sounds and Audio mmsys.cpl
Spider Solitare Card Game spider
SQL Client Configuration cliconfg
System Configuration Editor sysedit
System Configuration Utility msconfig
System File Checker Utility (Scan Immediately) sfc /scannow
System File Checker Utility (Scan Once At Next Boot) sfc /scanonce
System File Checker Utility (Scan On Every Boot) sfc /scanboot
System File Checker Utility (Return to Default Setting) sfc /revert
System File Checker Utility (Purge File Cache) sfc /purgecache
System File Checker Utility (Set Cache Size to size x) sfc /cachesize=x
System Properties sysdm.cpl
Task Manager taskmgr
Telnet Client telnet
User Account Management nusrmgr.cpl
Utility Manager utilman
Windows Firewall firewall.cpl
Windows Magnifier magnify
Windows Management Infrastructure wmimgmt.msc
Windows System Security Tool syskey
Windows Update Launches wupdmgr
Windows XP Tour Wizard tourstart
Wordpad write
Enable Task Manager
Method 1
Click Start, Run and type this command exactly as given below: (better - Copy and paste)
Method 2
Download and run this REG fix and double-click it.
Method 3
• Click Start, Run and type Regedit.exe
• Navigate to the following branch:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Policies\ System
• In the right-pane, delete the value named DisableTaskMgr
• Close Regedit.exe
To hide a folder
1. Ha! this thing is way 2 old now!I know a much powerful trick 2 hide a folder!Follow these steps—-
1.Right click on the folder u want 2 hide.
2.go on 2 “Rename” option on the list.
3.Now press this combination—
Alt+2,5,5
Note—–The 2,5,5 numbers r 2 b used from the number pad on the right side of the keyboard and not from the horizontal pad provided just below the F1,F2,F3……..keys.
This will erase out the name of the folder.
4.to hide the picture of the folder. right click again and this time….select properties on the menu.
5.After the dialog box appears..click on the “customize”tab {the last tab at the top}, and click on “change icon” at the bottom of the dialog box,which is written at the left of a folder picture.
6.After the appearance of the “change icon” dialog box….click on any area within the dialog box,which seems “blank” and press ok.
7.come back 2 the dialog box { 2 the 1 from where u started..:p} and then select apply and then ok.
8.Happy playin’ hide-and-seek wid your foldrs!
9.2 unhide, refresh the screen.
10.u may see the hidden folder blinkin’ everytime the screen is refreshed.
11.go to the place where u see the folder blinkin’ and press right mouse button.
12.Again select “rename” and rename the folder.
13. Again go 2 properties and repeat step 4 to 6 but……instead of selectin’ a blank space,select ne other pic. a nd press ok..!!!
Click Start, Run and type this command exactly as given below: (better - Copy and paste)
Method 2
Download and run this REG fix and double-click it.
Method 3
• Click Start, Run and type Regedit.exe
• Navigate to the following branch:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Policies\ System
• In the right-pane, delete the value named DisableTaskMgr
• Close Regedit.exe
To hide a folder
1. Ha! this thing is way 2 old now!I know a much powerful trick 2 hide a folder!Follow these steps—-
1.Right click on the folder u want 2 hide.
2.go on 2 “Rename” option on the list.
3.Now press this combination—
Alt+2,5,5
Note—–The 2,5,5 numbers r 2 b used from the number pad on the right side of the keyboard and not from the horizontal pad provided just below the F1,F2,F3……..keys.
This will erase out the name of the folder.
4.to hide the picture of the folder. right click again and this time….select properties on the menu.
5.After the dialog box appears..click on the “customize”tab {the last tab at the top}, and click on “change icon” at the bottom of the dialog box,which is written at the left of a folder picture.
6.After the appearance of the “change icon” dialog box….click on any area within the dialog box,which seems “blank” and press ok.
7.come back 2 the dialog box { 2 the 1 from where u started..:p} and then select apply and then ok.
8.Happy playin’ hide-and-seek wid your foldrs!
9.2 unhide, refresh the screen.
10.u may see the hidden folder blinkin’ everytime the screen is refreshed.
11.go to the place where u see the folder blinkin’ and press right mouse button.
12.Again select “rename” and rename the folder.
13. Again go 2 properties and repeat step 4 to 6 but……instead of selectin’ a blank space,select ne other pic. a nd press ok..!!!
VSS Client installation
VSS Client installation
1. Open VSS in client system.
2. Right click on project source, select “Set working Folder”.
3. Select the client system project folder to set the set working folder for vss to interact with the client to vss.
4. Create new folder(Ex:- Ad-Dashboard)
5. Right click on Project, select “Get Latest Version” to copy the server version of project to client system.
6. Open the project source folder.
7. Double click on Solution, it will open the project in Microsoft visual studio.
(Note:- The arrow symbols indicate that the project in vss).
8. The lock symbols indicate that the project is in vss and no other developer is check out the source.
9. If anybody check the source files, the right arrow symbol will be associated instead of lock symbol and the other developer will know that by a developer symbol is displayed instead of lock. Means that the other developer can view only, no permission to edit.
Rules to use the project which is deployed in vss:-
1. Always open the project with vss, open the vss solution only.
2. Check whether the code is updated, right click on the file which is updated and select “Get latest version(Recursive)”.
3. If you want to modify the source file, right click on the file select “Check out for edit”.
4. Add comment and click on “Check Out”.
5. A right symbol will be displayed instead of lock symbol.
6. And the other person will get the person symbol, indicates that he can’t modify only view it.
7. After code updation, right click on source file which he check out last time and again add comment on what he modified then click on “Check in”.
8. If he doesn’t want to modify the source file which he check out last time, right click on the file select “Undo check out”.
1. Open VSS in client system.
2. Right click on project source, select “Set working Folder”.
3. Select the client system project folder to set the set working folder for vss to interact with the client to vss.
4. Create new folder(Ex:- Ad-Dashboard)
5. Right click on Project, select “Get Latest Version” to copy the server version of project to client system.
6. Open the project source folder.
7. Double click on Solution, it will open the project in Microsoft visual studio.
(Note:- The arrow symbols indicate that the project in vss).
8. The lock symbols indicate that the project is in vss and no other developer is check out the source.
9. If anybody check the source files, the right arrow symbol will be associated instead of lock symbol and the other developer will know that by a developer symbol is displayed instead of lock. Means that the other developer can view only, no permission to edit.
Rules to use the project which is deployed in vss:-
1. Always open the project with vss, open the vss solution only.
2. Check whether the code is updated, right click on the file which is updated and select “Get latest version(Recursive)”.
3. If you want to modify the source file, right click on the file select “Check out for edit”.
4. Add comment and click on “Check Out”.
5. A right symbol will be displayed instead of lock symbol.
6. And the other person will get the person symbol, indicates that he can’t modify only view it.
7. After code updation, right click on source file which he check out last time and again add comment on what he modified then click on “Check in”.
8. If he doesn’t want to modify the source file which he check out last time, right click on the file select “Undo check out”.
VSS Server configuration
VSS Server configuration
1. Copy the project into the server (D:\Noah Projects\AD-Dashboard)
2. Open Visual studio 2005.
3. Create a blank solution.
4. Add existing project source to the solution. Right click on solution, select “Existing website”.
5. Now add project to the VSS. Right click on solution, select “Add solution to source control”.
6. Select the vss database then login as admin user.
7. Select the root folder to save the project in to vss.
8. Now the Project has been successfully added to VSS.
1. Copy the project into the server (D:\Noah Projects\AD-Dashboard)
2. Open Visual studio 2005.
3. Create a blank solution.
4. Add existing project source to the solution. Right click on solution, select “Existing website”.
5. Now add project to the VSS. Right click on solution, select “Add solution to source control”.
6. Select the vss database then login as admin user.
7. Select the root folder to save the project in to vss.
8. Now the Project has been successfully added to VSS.
CVS Installation
CVS Installation
1. Run the cvs server in the windows server 2003 32bit system.
2. Select “Complete”
3. After installation select “Start->Programs->CVSNT->CVSNT Control Panel
4. Select “Repository Configuration”
5. Click “Add” to create repository.
6. Select “Standard” as repository to give permissions to repository.
7. Select the repository location in server.
8. Give the name of the repository (\CVS).
9. Select “Server settings”.
10. Select the user administration as per domain.
The CVS server will be configured successfully.
11. After client installation, client need Net beans ide with cvs integration.
12. Open the Net beans, select “Versioning->Checkout” to get the source the
1. Run the cvs server in the windows server 2003 32bit system.
2. Select “Complete”
3. After installation select “Start->Programs->CVSNT->CVSNT Control Panel
4. Select “Repository Configuration”
5. Click “Add” to create repository.
6. Select “Standard” as repository to give permissions to repository.
7. Select the repository location in server.
8. Give the name of the repository (\CVS).
9. Select “Server settings”.
10. Select the user administration as per domain.
The CVS server will be configured successfully.
11. After client installation, client need Net beans ide with cvs integration.
12. Open the Net beans, select “Versioning->Checkout” to get the source the
Exchange Installation Requisites
Installation of Exchange 2007 on Windows Server 2008 64 Bit
Pre-Installation Checklist
Install Windows Server 2008 64 bit version
Configure your static IP address
Activate Auto Updates
Add role - Active Directory Services
Add role - Active Directory Lightweight Services
Add feature - Windows Process Activation Service
Add role - Web Server (IIS)
Add feature - Power Shell
Roles / Features NOT to install
Installing Exchange Server 2007
Allow IGetMail access to your Exchange Server
Adding E-Mail Users
*Note: Please Activate Windows Server with Licensed Key ( Right click on my computer System Properties and Activate)
Pre-Installation Checklist Make sure you have all of the following steps in place before you setup Exchange Server 2007 on Windows Server 2008 64 Bit. For simplicity we are assuming you are setting up a small office where one machine will be used for both the Active Directory and the Exchange Server. This setup works just fine and reduces the number of machines to maintain. If you have a larger office you may want to consider separating the Active Directory machine and the Exchange 2007 Server.
Install Windows Server 2008 64 bit version Exchange 2007 is a 64 bit application and requires 64 bit versions of Windows Server 2003 or Windows Server 2008. You should select a computer that is capable of running the 64 bit version of Windows Server 2003 or 2008. For this example we will start with a clean installation of Windows Server 2008 64 bit version that has not had any roles installed. After installing Windows Server 2008 we set the clock and the name of the server to be "EX2007". At this point this server is configured to be a stand alone computer with default settings.
Pre-Installation Checklist
Install Windows Server 2008 64 bit version
Configure your static IP address
Activate Auto Updates
Add role - Active Directory Services
Add role - Active Directory Lightweight Services
Add feature - Windows Process Activation Service
Add role - Web Server (IIS)
Add feature - Power Shell
Roles / Features NOT to install
Installing Exchange Server 2007
Allow IGetMail access to your Exchange Server
Adding E-Mail Users
*Note: Please Activate Windows Server with Licensed Key ( Right click on my computer System Properties and Activate)
Pre-Installation Checklist Make sure you have all of the following steps in place before you setup Exchange Server 2007 on Windows Server 2008 64 Bit. For simplicity we are assuming you are setting up a small office where one machine will be used for both the Active Directory and the Exchange Server. This setup works just fine and reduces the number of machines to maintain. If you have a larger office you may want to consider separating the Active Directory machine and the Exchange 2007 Server.
Install Windows Server 2008 64 bit version Exchange 2007 is a 64 bit application and requires 64 bit versions of Windows Server 2003 or Windows Server 2008. You should select a computer that is capable of running the 64 bit version of Windows Server 2003 or 2008. For this example we will start with a clean installation of Windows Server 2008 64 bit version that has not had any roles installed. After installing Windows Server 2008 we set the clock and the name of the server to be "EX2007". At this point this server is configured to be a stand alone computer with default settings.
Installation Guide for MOSS2007
Installation Guide for MOSS2007
Hardware requirements
Front-end Web server and application server computers: a dual-processor computer with processor clock speeds of 2.5-gigahertz (GHz) or higher and a minimum of 2 gigabytes (GB) of RAM.
Back-end database server: a dual-processor computer with processor clock speeds of 2.0 GHz or higher and a minimum of 2 GB of RAM.
Software requirements Web and Application Server
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 (Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, or Web Edition) with Service Pack 1 (SP1)
Microsoft .Net Framework 2.0
Microsoft .Net Framework 3.0
The Web server and application server computers must be configured as Web servers running Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) in IIS 6.0 worker process isolation mode.
Each of the computers must be using the NTFS file system. Windows Server 2003 includes a conversion utility (Convert.exe) that you can use to convert an existing file allocation table (FAT) volume to NTFS without losing data.
Back-End Database Server
The back-end database server computer must be running Microsoft SQL Server 2005 or Microsoft SQL Server 2000 with Service Pack 3 (SP3) or later. It is assumed that you have installed and configured the database program on the back-end server computer. You do not need to set up or create specific databases for Office SharePoint Server 2007. The Office SharePoint Server 2007 Setup program will create the necessary databases when you install and configure Office SharePoint Server 2007.
Install Windows .NET Framework 2.0
1. Run .Net Framework 2.0 Setup
Enable ASP.NET 2.0
1. Click Start, point to All Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
2. In the IIS Manager tree, click the plus sign ( ) next to the server name, and then click the Web Service Extensions folder.
3. In the details pane, click ASP.NET v2.0.50727, and then click Allow.
Install .Net Framework 3.0
1. Run .Net Framework 3.0 Setup
Install Microsoft Windows Workflow Foundation Runtime. Install and configure 2007 Office SharePoint Server
It is recommended that you install and configure Office SharePoint Server 2007 on all of your front-end servers before you configure Office SharePoint Server 2007 services and create sites. If you want to build a minimal server farm configuration, and incrementally add front-end servers to expand the farm, you can install and configure Office SharePoint Server 2007 on a single front-end server and configure the front-end server as both a Web server and an application server. Regardless how many front-end servers you have in your server farm, you must have SQL Server running on at least one back-end database server before you install Office SharePoint Server 2007 on your front-end servers.
Run 2007 Office SharePoint Server Setup
1. Run Officeserver.exe, on one of your Web server computers.
2. On the Enter your Product Key page, enter your product key and click Continue.
1. On the Read the Microsoft Software License Terms page, review the terms, select the I accept the terms of this agreement check box, and then click Continue.
4) On the Choose the installation you want page, click Advanced.
5. On the Server Type tab, do one of the following:
If you are setting up a computer that will act as an application server, or a Web server and an application server, click Complete, and then click Install Now.
If you are setting up a computer that will act as a Web server only, click Web Front End, and then click Install Now.
6. When Setup finishes, a dialog box appears telling you that you must complete the configuration of your server. Make sure that the Run the SharePoint Products and Technologies Configuration Wizard now check box is selected.
7. Click Close to start the configuration wizard. Instructions for completing the wizard are provided in the next set of steps.
8) restart the IIS.
****Installation Part is completed****
Go to Program Files-Microsoft office serversharepoint 3.0 central administration
Then Login with authentication
Username:kmipl\administrator
Password: p@sswd@123
Then you will be getting the central administration menu with url :http://km-sharepoint:40882
Click on Application Managementshare point web application management create or extend web applicationcreate a new web applicationcreate or extend web application.-select create a new web applicationin create a new web application ( do not change any fields) then press okselect template -->click ok.-->then go to IIS browse the website and check .
To restore the backup file follow the below procedure:
In command prompt these actions are to be performed:
C:/Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\web server extensions\12\BIN
stsadm -o restore -url http://km-sharepoint:7248/ -filename"D:\Anand\Talk about\talkabout.bak" -overwrite
Hardware requirements
Front-end Web server and application server computers: a dual-processor computer with processor clock speeds of 2.5-gigahertz (GHz) or higher and a minimum of 2 gigabytes (GB) of RAM.
Back-end database server: a dual-processor computer with processor clock speeds of 2.0 GHz or higher and a minimum of 2 GB of RAM.
Software requirements Web and Application Server
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 (Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, or Web Edition) with Service Pack 1 (SP1)
Microsoft .Net Framework 2.0
Microsoft .Net Framework 3.0
The Web server and application server computers must be configured as Web servers running Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) in IIS 6.0 worker process isolation mode.
Each of the computers must be using the NTFS file system. Windows Server 2003 includes a conversion utility (Convert.exe) that you can use to convert an existing file allocation table (FAT) volume to NTFS without losing data.
Back-End Database Server
The back-end database server computer must be running Microsoft SQL Server 2005 or Microsoft SQL Server 2000 with Service Pack 3 (SP3) or later. It is assumed that you have installed and configured the database program on the back-end server computer. You do not need to set up or create specific databases for Office SharePoint Server 2007. The Office SharePoint Server 2007 Setup program will create the necessary databases when you install and configure Office SharePoint Server 2007.
Install Windows .NET Framework 2.0
1. Run .Net Framework 2.0 Setup
Enable ASP.NET 2.0
1. Click Start, point to All Programs, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
2. In the IIS Manager tree, click the plus sign ( ) next to the server name, and then click the Web Service Extensions folder.
3. In the details pane, click ASP.NET v2.0.50727, and then click Allow.
Install .Net Framework 3.0
1. Run .Net Framework 3.0 Setup
Install Microsoft Windows Workflow Foundation Runtime. Install and configure 2007 Office SharePoint Server
It is recommended that you install and configure Office SharePoint Server 2007 on all of your front-end servers before you configure Office SharePoint Server 2007 services and create sites. If you want to build a minimal server farm configuration, and incrementally add front-end servers to expand the farm, you can install and configure Office SharePoint Server 2007 on a single front-end server and configure the front-end server as both a Web server and an application server. Regardless how many front-end servers you have in your server farm, you must have SQL Server running on at least one back-end database server before you install Office SharePoint Server 2007 on your front-end servers.
Run 2007 Office SharePoint Server Setup
1. Run Officeserver.exe, on one of your Web server computers.
2. On the Enter your Product Key page, enter your product key and click Continue.
1. On the Read the Microsoft Software License Terms page, review the terms, select the I accept the terms of this agreement check box, and then click Continue.
4) On the Choose the installation you want page, click Advanced.
5. On the Server Type tab, do one of the following:
If you are setting up a computer that will act as an application server, or a Web server and an application server, click Complete, and then click Install Now.
If you are setting up a computer that will act as a Web server only, click Web Front End, and then click Install Now.
6. When Setup finishes, a dialog box appears telling you that you must complete the configuration of your server. Make sure that the Run the SharePoint Products and Technologies Configuration Wizard now check box is selected.
7. Click Close to start the configuration wizard. Instructions for completing the wizard are provided in the next set of steps.
8) restart the IIS.
****Installation Part is completed****
Go to Program Files-Microsoft office serversharepoint 3.0 central administration
Then Login with authentication
Username:kmipl\administrator
Password: p@sswd@123
Then you will be getting the central administration menu with url :http://km-sharepoint:40882
Click on Application Managementshare point web application management create or extend web applicationcreate a new web applicationcreate or extend web application.-select create a new web applicationin create a new web application ( do not change any fields) then press okselect template -->click ok.-->then go to IIS browse the website and check .
To restore the backup file follow the below procedure:
In command prompt these actions are to be performed:
C:/Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\web server extensions\12\BIN
stsadm -o restore -url http://km-sharepoint:7248/ -filename"D:\Anand\Talk about\talkabout.bak" -overwrite
To Create User in CVS (JAVA)
The below is the cofiguration settings for the CVS user creaton :
Example:
d:\CVSNT --->Enter Key
set cvsroot = :SSPI:localhost:/km-repo
cvs ls
cvs passwd -r cvsuser -a username (as required)
enter password
confirm password
Example:
d:\CVSNT --->Enter Key
set cvsroot = :SSPI:localhost:/km-repo
cvs ls
cvs passwd -r cvsuser -a username (as required)
enter password
confirm password
Friday, August 6, 2010
To enable calender in user system after removing admin Rights in domain
Since there is a local security policy on each computer that allows/disallows setting the system time, you should be able to configure a group policy with the same effect. Below are instructions for how to set local system settings.
Setting system access permissions on Windows XP -
To set permissions on Windows XP:
1. Select Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. In the Control Panel, open Administrative Tools.
3. In Administrative Tools, open Local Security Policy.
4. In the Local Security Settings window, expand the tree for Local Policies and select User Rights Assignment.
5. Right-click the required user right, and select Properties. The appropriate properties window appears (for example, Change the system time).
6. To add permissions:
a. Click Add User or Group. The software opens the Select Users or Groups window.
b. Specify the user ID that requires this permission.
c. Click OK.
d. Click Apply then OK to save your changes and close the Properties window.
7. When you are finished, restart the machine so that the updates will take effect.
Also, here is a link to MS site on how to edit the registry to allow a user to access the time/calendar - http://support.microsoft.com/kb/300022
Hope that helps a bit.
localsecpolwinxp.gif (13.3 KB)
M
Setting system access permissions on Windows XP -
To set permissions on Windows XP:
1. Select Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. In the Control Panel, open Administrative Tools.
3. In Administrative Tools, open Local Security Policy.
4. In the Local Security Settings window, expand the tree for Local Policies and select User Rights Assignment.
5. Right-click the required user right, and select Properties. The appropriate properties window appears (for example, Change the system time).
6. To add permissions:
a. Click Add User or Group. The software opens the Select Users or Groups window.
b. Specify the user ID that requires this permission.
c. Click OK.
d. Click Apply then OK to save your changes and close the Properties window.
7. When you are finished, restart the machine so that the updates will take effect.
Also, here is a link to MS site on how to edit the registry to allow a user to access the time/calendar - http://support.microsoft.com/kb/300022
Hope that helps a bit.
localsecpolwinxp.gif (13.3 KB)
M
Thursday, July 29, 2010
Windows Server Support Interview Questions and Answers (L2)
Windows Server Support Interview Questions and Answers (L2)
What is the difference between Authorized DHCP and Non Authorized DHCP?
To avoid problems in the network causing by mis-configured DHCP servers, server in windows 2000 must be validate by AD before starting service to clients. If an authorized DHCP finds any DHCP server in the network it stop serving the clients
Difference between inter-site and intra-site replication. Protocols using for replication.
Intra-site replication can be done between the domain controllers in the same site. Inter-site replication can be done between two different sites over WAN links
BHS (Bridge Head Servers) is responsible for initiating replication between the sites. Inter-site replication can be done B/w BHS in one site and BHS in another site.
We can use RPC over IP or SMTP as a replication protocols where as Domain partition is not possible to replicate using SMTP
How to monitor replication
We can user Replmon tool from support tools
Brief explanation of RAID Levels
Microsoft Windows XP, Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 offer two types of disk storage: basic and dynamic.
Basic Disk Storage
Basic storage uses normal partition tables supported by MS-DOS, Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Windows 98, Microsoft Windows Millennium Edition (Me), Microsoft Windows NT, Microsoft Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP. A disk initialized for basic storage is called a basic disk. A basic disk contains basic volumes, such as primary partitions, extended partitions, and logical drives. Additionally, basic volumes include multidisk volumes that are created by using Windows NT 4.0 or earlier, such as volume sets, stripe sets, mirror sets, and stripe sets with parity. Windows XP does not support these multidisk basic volumes. Any volume sets, stripe sets, mirror sets, or stripe sets with parity must be backed up and deleted or converted to dynamic disks before you install Windows XP Professional.
Dynamic Disk Storage
Dynamic storage is supported in Windows XP Professional, Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003. A disk initialized for dynamic storage is called a dynamic disk. A dynamic disk contains dynamic volumes, such as simple volumes, spanned volumes, striped volumes, mirrored volumes, and RAID-5 volumes. With dynamic storage, you can perform disk and volume management without the need to restart Windows.
Note: Dynamic disks are not supported on portable computers or on Windows XP Home Edition-based computers.
You cannot create mirrored volumes or RAID-5 volumes on Windows XP Home Edition, Windows XP Professional, or Windows XP 64-Bit Edition-based computers. However, you can use a Windows XP Professional-based computer to create a mirrored or RAID-5 volume on remote computers that are running Windows 2000 Server, Windows 2000 Advanced Server, or Windows 2000 Datacenter Server, or the Standard, Enterprise and Data Center versions of Windows Server 2003.
Storage types are separate from the file system type. A basic or dynamic disk can contain any combination of FAT16, FAT32, or NTFS partitions or volumes.
A disk system can contain any combination of storage types. However, all volumes on the same disk must use the same storage type.
To convert a Basic Disk to a Dynamic Disk:
Use the Disk Management snap-in in Windows XP/2000/2003 to convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Log on as Administrator or as a member of the Administrators group.
2. Click Start, and then click Control Panel.
3. Click Performance and Maintenance, click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Computer Management. You can also right-click My Computer and choose Manage if you have My Computer displayed on your desktop.
4. In the left pane, click Disk Management.
5. In the lower-right pane, right-click the basic disk that you want to convert, and then click Convert to Dynamic Disk. You must right-click the gray area that contains the disk title on the left side of the Details pane.
6. Select the check box that is next to the disk that you want to convert (if it is not already selected), and then click OK.
7. Click Details if you want to view the list of volumes in the disk. Click Convert.
8. Click Yes when you are prompted to convert the disk, and then click OK.
Warning: After you convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk, local access to the dynamic disk is limited to Windows XP Professional, Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003. Additionally, after you convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk, the dynamic volumes cannot be changed back to partitions. You must first delete all dynamic volumes on the disk and then convert the dynamic disk back to a basic disk. If you want to keep your data, you must first back up the data or move it to another volume.
Dynamic Storage Terms
A volume is a storage unit made from free space on one or more disks. It can be formatted with a file system and assigned a drive letter. Volumes on dynamic disks can have any of the following layouts: simple, spanned, mirrored, striped, or RAID-5.
A simple volume uses free space from a single disk. It can be a single region on a disk or consist of multiple, concatenated regions. A simple volume can be extended within the same disk or onto additional disks. If a simple volume is extended across multiple disks, it becomes a spanned volume.
A spanned volume is created from free disk space that is linked together from multiple disks. You can extend a spanned volume onto a maximum of 32 disks. A spanned volume cannot be mirrored and is not fault-tolerant.
A striped volume is a volume whose data is interleaved across two or more physical disks. The data on this type of volume is allocated alternately and evenly to each of the physical disks. A striped volume cannot be mirrored or extended and is not fault-tolerant. Striping is also known as RAID-0.
A mirrored volume is a fault-tolerant volume whose data is duplicated on two physical disks. All of the data on one volume is copied to another disk to provide data redundancy. If one of the disks fails, the data can still be accessed from the remaining disk. A mirrored volume cannot be extended. Mirroring is also known as RAID-1.
A RAID-5 volume is a fault-tolerant volume whose data is striped across an array of three or more disks. Parity (a calculated value that can be used to reconstruct data after a failure) is also striped across the disk array. If a physical disk fails, the portion of the RAID-5 volume that was on that failed disk can be re-created from the remaining data and the parity. A RAID-5 volume cannot be mirrored or extended.
The system volume contains the hardware-specific files that are needed to load Windows (for example, Ntldr, Boot.ini, and Ntdetect.com). The system volume can be, but does not have to be, the same as the boot volume.
The boot volume contains the Windows operating system files that are located in the %Systemroot% and %Systemroot%\System32 folders. The boot volume can be, but does not have to be, the same as the system volume.
RAID 0 – Striping
RAID 1- Mirroring (minimum 2 HDD required)
RAID 5 – Striping With Parity (Minimum 3 HDD required)
RAID levels 1 and 5 only gives redundancy
What are the different backup strategies are available
Normal Backup
Incremental Backup
Differential Backup
Daily Backup
Copy Backup
What is a global catalog
Global catalog is a role, which maintains Indexes about objects. It contains full information of the objects in its own domain and partial information of the objects in other domains. Universal Group membership information will be stored in global catalog servers and replicate to all GC’s in the forest.
What is Active Directory and what is the use of it
Active directory is a directory service, which maintains the relation ship between resources and enabling them to work together. Because of AD hierarchal structure windows 2000 is more scalable, reliable. Active directory is derived from X.500 standards where information is stored is hierarchal tree like structure. Active directory depends on two Internet standards one is DNS and other is LDAP. Information in Active directory can be queried by using LDAP protocol
What is the physical and logical structure of AD?
Active directory physical structure is a hierarchal structure which fallows Forests—Trees—Domains—Child Domains—Grand Child—etc
Active directory is logically divided into 3 partitions
1.Configuration partition 2. Schema Partition 3. Domain partition 4. Application Partition (only in windows 2003 not available in windows 2000)
Out of these Configuration, Schema partitions can be replicated between the domain controllers in the in the entire forest. Where as Domain partition can be replicated between the domain controllers in the same domain
What is the process of user authentication (Kerberos V5) in windows 2000?
After giving logon credentials an encryption key will be generated which is used to encrypt the time stamp of the client machine. User name and encrypted timestamp information will be provided to domain controller for authentication. Then Domain controller based on the password information stored in AD for that user it decrypts the encrypted time stamp information. If produces time stamp matches to its time stamp. It will provide logon session key and Ticket granting ticket to client in an encryption format. Again client decrypts and if produced time stamp information is matching then it will use logon session key to logon to the domain. Ticket granting ticket will be used to generate service granting ticket when accessing network resources
What are the port numbers for Kerberos, LDAP and Global Catalog?
Kerberos – 88, LDAP – 389, Global Catalog – 3268
What is the use of LDAP (X.500 standard?)
LDAP is a directory access protocol, which is used to exchange directory information from server to clients or from server to servers
What are the problems that are generally come across DHCP?
Scope is full with IP addresses no IP’s available for new machines
If scope options are not configured properly eg default gateway
Incorrect creation of scopes etc
What is the role responsible for time synchronization?
PDC Emulator is responsible for time synchronization. Time synchronization is important because Kerberos authentication depends on time stamp information
What is TTL & how to set TTL time in DNS?
TTL is Time to Live setting used for the amount of time that the record should remain in cache when name resolution happened.
We can set TTL in SOA (start of authority record) of DNS
How to take DNS and WINS, DHCP backup
%System root%/system32/dns
%System root%/system32/WINS
%System root%/system32/DHCP
What is recovery console
Recovery console is a utility used to recover the system when it is not booting properly or not at all booting. We can perform fallowing operations from recovery console
We can copy, rename, or replace operating system files and folders
Enable or disable service or device startup the next time that start computer
Repair the file system boot sector or the Master Boot Record
Create and format partitions on drives
What is DFS & its usage
DFS is a distributed file system used to provide common environment for users to access files and folders even when they are shared in different servers physically.
There are two types of DFS domain DFS and Stand alone DFS. We cannot provide redundancy for stand alone DFS in case of failure. Domain DFS is used in a domain environment which can be accessed by /domain name/root1 (root 1 is DFS root name). Stand alone DFS can be used in workgroup environment which can be accessed through /server name/root1 (root 1 is DFS root name). Both the cases we need to create DFS root ( Which appears like a shared folder for end users) and DFS links ( A logical link which is pointing to the server where the folder is physically shared)
The maximum number of Dfs roots per server is 1.
The maximum numbers of Dfs root replicas are 31.
The maximum number of Dfs roots per domain is unlimited.
The maximum number of Dfs links or shared folders in a Dfs root is 1,000
What is RIS and what are its requirements
RIS is a remote installation service, which is used to install operation system remotely.
Client requirements
PXE DHCP-based boot ROM version 1.00 or later NIC, or a network adapter that is supported by the RIS boot disk.
Should meet minimum operating system requirements
Software Requirements
Below network services must be active on RIS server or any server in the network
Domain Name System (DNS Service)
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Active directory “Directory” service
How many root replicas can be created in DFS?
31
What is the difference between Domain DFS and Standalone DFS?
Refer question 17.
High Level
Can we establish trust relationship between two forests?
In Windows 2000 it is not possible. In Windows 2003 it is possible
What is FSMO Roles
Flexible single master operation (FSMO) roles are
Domain Naming Master
Schema Master
PDC Emulator
Infrastructure Master
RID Master
Brief all the FSMO Roles
Windows 2000/2003 Multi-Master Model
A multi-master enabled database, such as the Active Directory, provides the flexibility of allowing changes to occur at any DC in the enterprise, but it also introduces the possibility of conflicts that can potentially lead to problems once the data is replicated to the rest of the enterprise. One way Windows 2000/2003 deals with conflicting updates is by having a conflict resolution algorithm handle discrepancies in values by resolving to the DC to which changes were written last (that is, "the last writer wins"), while discarding the changes in all other DCs. Although this resolution method may be acceptable in some cases, there are times when conflicts are just too difficult to resolve using the "last writer wins" approach. In such cases, it is best to prevent the conflict from occurring rather than to try to resolve it after the fact.
For certain types of changes, Windows 2000/2003 incorporates methods to prevent conflicting Active Directory updates from occurring.
Windows 2000/2003 Single-Master Model
To prevent conflicting updates in Windows 2000/2003, the Active Directory performs updates to certain objects in a single-master fashion.
In a single-master model, only one DC in the entire directory is allowed to process updates. This is similar to the role given to a primary domain controller (PDC) in earlier versions of Windows (such as Microsoft Windows NT 4.0), in which the PDC is responsible for processing all updates in a given domain.
In a forest, there are five FSMO roles that are assigned to one or more domain controllers. The five FSMO roles are:
Schema Master:
The schema master domain controller controls all updates and modifications to the schema. Once the Schema update is complete, it is replicated from the schema master to all other DCs in the directory. To update the schema of a forest, you must have access to the schema master. There can be only one schema master in the whole forest.
Domain naming master:
The domain naming master domain controller controls the addition or removal of domains in the forest. This DC is the only one that can add or remove a domain from the directory. It can also add or remove cross references to domains in external directories. There can be only one domain naming master in the whole forest.
Infrastructure Master:
When an object in one domain is referenced by another object in another domain, it represents the reference by the GUID, the SID (for references to security principals), and the DN of the object being referenced. The infrastructure FSMO role holder is the DC responsible for updating an object's SID and distinguished name in a cross-domain object reference. At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the infrastructure master in each domain.
Note: The Infrastructure Master (IM) role should be held by a domain controller that is not a Global Catalog server (GC). If the Infrastructure Master runs on a Global Catalog server it will stop updating object information because it does not contain any references to objects that it does not hold. This is because a Global Catalog server holds a partial replica of every object in the forest. As a result, cross-domain object references in that domain will not be updated and a warning to that effect will be logged on that DC's event log. If all the domain controllers in a domain also host the global catalog, all the domain controllers have the current data, and it is not important which domain controller holds the infrastructure master role.
Relative ID (RID) Master:
The RID master is responsible for processing RID pool requests from all domain controllers in a particular domain. When a DC creates a security principal object such as a user or group, it attaches a unique Security ID (SID) to the object. This SID consists of a domain SID (the same for all SIDs created in a domain), and a relative ID (RID) that is unique for each security principal SID created in a domain. Each DC in a domain is allocated a pool of RIDs that it is allowed to assign to the security principals it creates. When a DC's allocated RID pool falls below a threshold, that DC issues a request for additional RIDs to the domain's RID master. The domain RID master responds to the request by retrieving RIDs from the domain's unallocated RID pool and assigns them to the pool of the requesting DC. At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the RID master in the domain.
PDC Emulator:
The PDC emulator is necessary to synchronize time in an enterprise. Windows 2000/2003 includes the W32Time (Windows Time) time service that is required by the Kerberos authentication protocol. All Windows 2000/2003-based computers within an enterprise use a common time. The purpose of the time service is to ensure that the Windows Time service uses a hierarchical relationship that controls authority and does not permit loops to ensure appropriate common time usage.
The PDC emulator of a domain is authoritative for the domain. The PDC emulator at the root of the forest becomes authoritative for the enterprise, and should be configured to gather the time from an external source. All PDC FSMO role holders follow the hierarchy of domains in the selection of their in-bound time partner.
In a Windows 2000/2003 domain, the PDC emulator role holder retains the following functions:
Password changes performed by other DCs in the domain are replicated preferentially to the PDC emulator.
Authentication failures that occur at a given DC in a domain because of an incorrect password are forwarded to the PDC emulator before a bad password failure message is reported to the user.
Account lockout is processed on the PDC emulator.
Editing or creation of Group Policy Objects (GPO) is always done from the GPO copy found in the PDC Emulator's SYSVOL share, unless configured not to do so by the administrator.
The PDC emulator performs all of the functionality that a Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 Server-based PDC or earlier PDC performs for Windows NT 4.0-based or earlier clients.
This part of the PDC emulator role becomes unnecessary when all workstations, member servers, and domain controllers that are running Windows NT 4.0 or earlier are all upgraded to Windows 2000/2003. The PDC emulator still performs the other functions as described in a Windows 2000/2003 environment.
At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the PDC emulator master in each domain in the forest.
How to manually configure FSMO Roles to separate DC’s
How can I determine who are the current FSMO Roles holders in my domain/forest?
Windows 2000/2003 Active Directory domains utilize a Single Operation Master method called FSMO (Flexible Single Master Operation), as described in Understanding FSMO Roles in Active Directory.
The five FSMO roles are:
• Schema master - Forest-wide and one per forest.
• Domain naming master - Forest-wide and one per forest.
• RID master - Domain-specific and one for each domain.
• PDC - PDC Emulator is domain-specific and one for each domain.
• Infrastructure master - Domain-specific and one for each domain.
In most cases an administrator can keep the FSMO role holders (all 5 of them) in the same spot (or actually, on the same DC) as has been configured by the Active Directory installation process. However, there are scenarios where an administrator would want to move one or more of the FSMO roles from the default holder DC to a different DC. The transferring method is described in the Transferring FSMO Roles article, while seizing the roles from a non-operational DC to a different DC is described in the Seizing FSMO Roles article.
In order to better understand your AD infrastructure and to know the added value that each DC might possess, an AD administrator must have the exact knowledge of which one of the existing DCs is holding a FSMO role, and what role it holds. With that knowledge in hand, the administrator can make better arrangements in case of a scheduled shut-down of any given DC, and better prepare him or herself in case of a non-scheduled cease of operation from one of the DCs.
How to find out which DC is holding which FSMO role? Well, one can accomplish this task by many means. This article will list a few of the available methods.
Method #1: Know the default settings
The FSMO roles were assigned to one or more DCs during the DCPROMO process. The following table summarizes the FSMO default locations:
FSMO Role Number of DCs holding this role Original DC holding the FSMO role
Schema One per forest The first DC in the first domain in the forest (i.e. the Forest Root Domain)
Domain Naming One per forest
RID One per domain The first DC in a domain (any domain, including the Forest Root Domain, any Tree Root Domain, or any Child Domain)
PDC Emulator One per domain
Infrastructure One per domain
Method #2: Use the GUI
The FSMO role holders can be easily found by use of some of the AD snap-ins. Use this table to see which tool can be used for what FSMO role:
FSMO Role Which snap-in should I use?
Schema Schema snap-in
Domain Naming AD Domains and Trusts snap-in
RID AD Users and Computers snap-in
PDC Emulator
Infrastructure
Finding the RID Master, PDC Emulator, and Infrastructure Masters via GUI
To find out who currently holds the Domain-Specific RID Master, PDC Emulator, and Infrastructure Master FSMO Roles:
1. Open the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in from the Administrative Tools folder.
2. Right-click the Active Directory Users and Computers icon again and press Operation Masters.
3. Select the appropriate tab for the role you wish to view.
4. When you're done click close.
Finding the Domain Naming Master via GUI
To find out who currently holds the Domain Naming Master Role:
1. Open the Active Directory Domains and Trusts snap-in from the Administrative Tools folder.
2. Right-click the Active Directory Domains and Trusts icon again and press Operation Masters.
3. When you're done click close.
Finding the Schema Master via GUI
To find out who currently holds the Schema Master Role:
1. Register the Schmmgmt.dll library by pressing Start > RUN and typing:
2. Press OK. You should receive a success confirmation.
3. From the Run command open an MMC Console by typing MMC.
4. On the Console menu, press Add/Remove Snap-in.
5. Press Add. Select Active Directory Schema.
6. Press Add and press Close. Press OK.
7. Click the Active Directory Schema icon. After it loads right-click it and press Operation Masters.
8. Press the Close button.
Method #3: Use the Ntdsutil command
The FSMO role holders can be easily found by use of the Ntdsutil command.
Caution: Using the Ntdsutil utility incorrectly may result in partial or complete loss of Active Directory functionality.
1. On any domain controller, click Start, click Run, type Ntdsutil in the Open box, and then click OK.
2. Type roles, and then press ENTER.
Note: To see a list of available commands at any of the prompts in the Ntdsutil tool, type ?, and then press ENTER.
3. Type connections, and then press ENTER.
4. Type connect to server , where is the name of the server you want to use, and then press ENTER.
5. At the server connections: prompt, type q, and then press ENTER again.
6. At the FSMO maintenance: prompt, type Select operation target, and then press ENTER again.
At the select operation target: prompt, type List roles for connected server, and then press ENTER again.
select operation target: List roles for connected server
Server "server100" knows about 5 roles
Schema - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=C
onfiguration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
Domain - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=C
onfiguration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
PDC - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Conf
iguration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
RID - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Conf
iguration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
Infrastructure - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Si
tes,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
select operation target:
8. Type q 3 times to exit the Ntdsutil prompt.
Note: You can download THIS nice batch file that will do all this for you (1kb).
Another Note: Microsoft has a nice tool called Dumpfsmos.cmd, found in the Windows 2000 Resource Kit (and can be downloaded here: Download Free Windows 2000 Resource Kit Tools). This tool is basically a one-click Ntdsutil script that performs the same operation described above.
Method #4: Use the Netdom command
The FSMO role holders can be easily found by use of the Netdom command.
Netdom.exe is a part of the Windows 2000/XP/2003 Support Tools. You must either download it separately (from here Download Free Windows 2000 Resource Kit Tools) or by obtaining the correct Support Tools pack for your operating system. The Support Tools pack can be found in the \Support\Tools folder on your installation CD (or you can Download Windows 2000 SP4 Support Tools, Download Windows XP SP1 Deploy Tools).
1. On any domain controller, click Start, click Run, type CMD in the Open box, and then click OK.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type netdom query /domain: fsmo (where is the name of YOUR domain).
Close the CMD window.
Note: You can download THIS nice batch file that will do all this for you (1kb).
Method #5: Use the Replmon tool
The FSMO role holders can be easily found by use of the Netdom command.
Just like Netdom, Replmon.exe is a part of the Windows 2000/XP/2003 Support Tools. Replmon can be used for a wide verity of tasks, mostly with those that are related with AD replication. But Replmon can also provide valuable information about the AD, about any DC, and also about other objects and settings, such as GPOs and FSMO roles. Install the package before attempting to use the tool.
1. On any domain controller, click Start, click Run, type REPLMON in the Open box, and then click OK.
2. Right-click Monitored servers and select Add Monitored Server.
3. In the Add Server to Monitor window, select the Search the Directory for the server to add. Make sure your AD domain name is listed in the drop-down list.
4. In the site list select your site, expand it, and click to select the server you want to query. Click Finish.
5. Right-click the server that is now listed in the left-pane, and select Properties.
6. Click on the FSMO Roles tab and read the results.
7. Click Ok when you're done.
How can I forcibly transfer (seize) some or all of the FSMO Roles from one DC to another?
Windows 2000/2003 Active Directory domains utilize a Single Operation Master method called FSMO (Flexible Single Master Operation), as described in Understanding FSMO Roles in Active Directory.
The five FSMO roles are:
• Schema master - Forest-wide and one per forest.
• Domain naming master - Forest-wide and one per forest.
• RID master - Domain-specific and one for each domain.
• PDC - PDC Emulator is domain-specific and one for each domain.
• Infrastructure master - Domain-specific and one for each domain.
In most cases an administrator can keep the FSMO role holders (all 5 of them) in the same spot (or actually, on the same DC) as has been configured by the Active Directory installation process. However, there are scenarios where an administrator would want to move one or more of the FSMO roles from the default holder DC to a different DC.
Moving the FSMO roles while both the original FSMO role holder and the future FSMO role holder are online and operational is called Transferring, and is described in the Transferring FSMO Roles article.
However, when the original FSMO role holder went offline or became non operational for a long period of time, the administrator might consider moving the FSMO role from the original, non-operational holder, to a different DC. The process of moving the FSMO role from a non-operational role holder to a different DC is called Seizing, and is described in this article.
If a DC holding a FSMO role fails, the best thing to do is to try and get the server online again. Since none of the FSMO roles are immediately critical (well, almost none, the loss of the PDC Emulator FSMO role might become a problem unless you fix it in a reasonable amount of time), so it is not a problem to them to be unavailable for hours or even days.
If a DC becomes unreliable, try to get it back on line, and transfer the FSMO roles to a reliable computer. Administrators should use extreme caution in seizing FSMO roles. This operation, in most cases, should be performed only if the original FSMO role owner will not be brought back into the environment. Only seize a FSMO role if absolutely necessary when the original role holder is not connected to the network.
What will happen if you do not perform the seize in time? This table has the info:
FSMO Role Loss implications
Schema The schema cannot be extended. However, in the short term no one will notice a missing Schema Master unless you plan a schema upgrade during that time.
Domain Naming Unless you are going to run DCPROMO, then you will not miss this FSMO role.
RID Chances are good that the existing DCs will have enough unused RIDs to last some time, unless you're building hundreds of users or computer object per week.
PDC Emulator Will be missed soon. NT 4.0 BDCs will not be able to replicate, there will be no time synchronization in the domain, you will probably not be able to change or troubleshoot group policies and password changes will become a problem.
Infrastructure Group memberships may be incomplete. If you only have one domain, then there will be no impact.
Important: If the RID, Schema, or Domain Naming FSMOs are seized, then the original domain controller must not be activated in the forest again. It is necessary to reinstall Windows if these servers are to be used again.
The following table summarizes the FSMO seizing restrictions:
FSMO Role Restrictions
Schema Original must be reinstalled
Domain Naming
RID
PDC Emulator Can transfer back to original
Infrastructure
Another consideration before performing the seize operation is the administrator's group membership, as this table lists:
FSMO Role Administrator must be a member of
Schema Schema Admins
Domain Naming Enterprise Admins
RID Domain Admins
PDC Emulator
Infrastructure
To seize the FSMO roles by using Ntdsutil, follow these steps:
Caution: Using the Ntdsutil utility incorrectly may result in partial or complete loss of Active Directory functionality.
1. On any domain controller, click Start, click Run, type Ntdsutil in the Open box, and then click OK.
2. Type roles, and then press ENTER.
Note: To see a list of available commands at any of the prompts in the Ntdsutil tool, type ?, and then press ENTER.
3. Type connections, and then press ENTER.
4. Type connect to server , where is the name of the server you want to use, and then press ENTER.
5. At the server connections: prompt, type q, and then press ENTER again.
6. Type seize , where is the role you want to seize. For example, to seize the RID Master role, you would type seize rid master:
Options are:
7. You will receive a warning window asking if you want to perform the seize. Click on Yes.
fsmo maintenance: Seize infrastructure master
Attempting safe transfer of infrastructure FSMO before seizure.
ldap_modify_sW error 0x34(52 (Unavailable).
Ldap extended error message is 000020AF: SvcErr: DSID-03210300, problem 5002 (UNAVAILABLE)
data 1722
Win32 error returned is 0x20af(The requested FSMO operation failed. The current FSMO holde
r could not be contacted.)
)
Depending on the error code this may indicate a connection,
ldap, or role transfer error.
Transfer of infrastructure FSMO failed, proceeding with seizure ...
Server "server100" knows about 5 roles
Schema - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER200,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=netDomain - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
PDC - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
RID - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER200,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
Infrastructure - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
fsmo maintenance:
Note: All five roles need to be in the forest. If the first domain controller is out of the forest then seize all roles. Determine which roles are to be on which remaining domain controllers so that all five roles are not on only one server.
8. Repeat steps 6 and 7 until you've seized all the required FSMO roles.
9. After you seize or transfer the roles, type q, and then press ENTER until you quit the Ntdsutil tool.
Note: Do not put the Infrastructure Master (IM) role on the same domain controller as the Global Catalog server. If the Infrastructure Master runs on a GC server it will stop updating object information because it does not contain any references to objects that it does not hold. This is because a GC server holds a partial replica of every object in the forest.
What is the difference between authoritative and non-authoritative restore
In authoritative restore, Objects that are restored will be replicated to all domain controllers in the domain. This can be used specifically when the entire OU is disturbed in all domain controllers or specifically restore a single object, which is disturbed in all DC’s
In non-authoritative restore, Restored directory information will be updated by other domain controllers based on the latest modification time.
What is Active Directory De-fragmentation?
De-fragmentation of AD means separating used space and empty space created by deleted objects and reduces directory size (only in offline De-fragmentation)
Difference between online and offline de-fragmentation
The size of NTDS.DIT will often be different sizes across the domain controllers in a domain. Remember that Active Directory is a multi-master independent model where updates are occurring in each of the domain controllers with the changes being replicated over time to the other domain controllers.
The changed data is replicated between domain controllers, not the database, so there is no guarantee that the files are going to be the same size across all domain controllers.
Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 servers running Directory Services (DS) perform a directory online defragmentation every 12 hours by default as part of the garbage-collection process. This defragmentation only moves data around the database file (NTDS.DIT) and doesn’t reduce the file’s size - the database file cannot be compacted while Active Directory is mounted.
Active Directory routinely performs online database defragmentation, but this is limited to the disposal of tombstoned objects. The database file cannot be compacted while Active Directory is mounted (or online).
An NTDS.DIT file that has been defragmented offline (compacted), can be much smaller than the NTDS.DIT file on its peers.
However, defragmenting the NTDS.DIT file isn’t something you should really need to do. Normally, the database self-tunes and automatically tombstoning the records then sweeping them away when the tombstone lifetime has passed to make that space available for additional records.
Defragging the NTDS.DIT file probably won’t help your AD queries go any faster in the long run.
So why defrag it in the first place?
One reason you might want to defrag your NTDS.DIT file is to save space, for example if you deleted a large number of records at one time.
To create a new, smaller NTDS.DIT file and to enable offline defragmentation, perform the following steps:
Back up Active Directory (AD).
Reboot the server, select the OS option, and press F8 for advanced options.
Select the Directory Services Restore Mode option, and press Enter. Press
Enter again to start the OS.
W2K will start in safe mode, with no DS running.
Use the local SAM’s administrator account and password to log on.
You’ll see a dialog box that says you’re in safe mode. Click OK.
From the Start menu, select Run and type cmd.exe
In the command window, you’ll see the following text. (Enter the commands in bold.)
C:\> ntdsutil
ntdsutil: files
file maintenance:info
....
file maintenance:compact to c:\temp
You’ll see the defragmentation process. If the process was successful, enter quit to return to the command prompt.
Then, replace the old NTDS.DIT file with the new, compressed version. (Enter the commands in bold.)
C:\> copy c:\temp\ntds.dit %systemroot%\ntds\ntds.dit
Restart the computer, and boot as normal.
What is tombstone period
Tombstones are nothing but objects marked for deletion. After deleting an object in AD the objects will not be deleted permanently. It will be remain 60 days by default (which can be configurable) it adds an entry as marked for deletion on the object and replicates to all DC’s. After 60 days object will be deleted permanently from all Dc’s.
What is white space and Garbage Collection?
refer question 7
What are the monitoring tools used for Server and Network Heath. How to define alert mechanism
Spot Light , SNMP Need to enable .
How to deploy the patches and what are the softwares used for this process
Using SUS (Software update services) server we can deploy patches to all clients in the network. We need to configure an option called “Synchronize with Microsoft software update server” option and schedule time to synchronize in server. We need to approve new update based on the requirement. Then approved update will be deployed to clients
We can configure clients by changing the registry manually or through Group policy by adding WUAU administrative template in group policy
What is Clustering. Briefly define & explain it
Clustering is a technology, which is used to provide High Availability for mission critical applications. We can configure cluster by installing MCS (Microsoft cluster service) component from Add remove programs, which can only available in Enterprise Edition and Data center edition.
In Windows we can configure two types of clusters
NLB (network load balancing) cluster for balancing load between servers. This cluster will not provide any high availability. Usually preferable at edge servers like web or proxy.
Server Cluster: This provides High availability by configuring active-active or active-passive cluster. In 2 node active-passive cluster one node will be active and one node will be stand by. When active server fails the application will FAILOVER to stand by server automatically. When the original server backs we need to FAILBACK the application
Quorum: A shared storage need to provide for all servers which keeps information about clustered application and session state and is useful in FAILOVER situation. This is very important if Quorum disk fails entire cluster will fails
Heartbeat: Heartbeat is a private connectivity between the servers in the cluster, which is used to identify the status of other servers in cluster.
How to configure SNMP
SNMP can be configured by installing SNMP from Monitoring and Management tools from Add and Remove programs.
For SNMP programs to communicate we need to configure common community name for those machines where SNMP programs (eg DELL OPEN MANAGER) running. This can be configured from services.msc--- SNMP service -- Security
Is it possible to rename the Domain name & how?
In Windows 2000 it is not possible. In windows 2003 it is possible. On Domain controller by going to MYCOMPUTER properties we can change.
What is SOA Record
SOA is a Start Of Authority record, which is a first record in DNS, which controls the startup behavior of DNS. We can configure TTL, refresh, and retry intervals in this record.
What is a Stub zone and what is the use of it.
Stub zones are a new feature of DNS in Windows Server 2003 that can be used to streamline name resolution, especially in a split namespace scenario. They also help reduce the amount of DNS traffic on your network, making DNS more efficient especially over slow WAN links.
What are the different types of partitions present in AD?
Active directory is divided into three partitions
Configuration Partition—replicates entire forest
Schema Partition—replicates entire forest
Domain Partition—replicate only in domain
Application Partition (Only in Windows 2003)
What are the (two) services required for replication
File Replication Service (FRS)
Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC)
Can we use a Linux DNS Sever in 2000 Domain?
We can use, But the BIND version should be 8 or greater
What is the difference between IIS Version 5 and IIS Version 6?
Refer Question 1
What is ASR (Automated System Recovery) and how to implement it
ASR is a two-part system; it includes ASR backup and ASR restore. The ASR Wizard, located in Backup, does the backup portion. The wizard backs up the system state, system services, and all the disks that are associated with the operating system components. ASR also creates a file that contains information about the backup, the disk configurations (including basic and dynamic volumes), and how to perform a restore.
You can access the restore portion by pressing F2 when prompted in the text-mode portion of setup. ASR reads the disk configurations from the file that it creates. It restores all the disk signatures, volumes, and partitions on (at a minimum) the disks that you need to start the computer. ASR will try to restore all the disk configurations, but under some circumstances it might not be able to. ASR then installs a simple installation of Windows and automatically starts a restoration using the backup created by the ASR Wizard.
What are the different levels that we can apply Group Policy
We can apply group policy at SITE level---Domain Level---OU level
What is Domain Policy, Domain controller policy, Local policy and Group policy
Domain Policy will apply to all computers in the domain, because by default it will be associated with domain GPO, Where as Domain controller policy will be applied only on domain controller. By default domain controller security policy will be associated with domain controller GPO. Local policy will be applied to that particular machine only and effects to that computer only.
What is the use of SYSVOL FOLDER?
Policies and scripts saved in SYSVOL folder will be replicated to all domain controllers in the domain. FRS (File replication service) is responsible for replicating all policies and scripts
What is folder redirection?
Folder Redirection is a User group policy. Once you create the group policy and link it to the appropriate folder object, an administrator can designate which folders to redirect and where To do this, the administrator needs to navigate to the following location in the Group Policy Object:
User Configuration\Windows Settings\Folder Redirection
In the Properties of the folder, you can choose Basic or Advanced folder redirection, and you can designate the server file system path to which the folder should be redirected.
The %USERNAME% variable may be used as part of the redirection path, thus allowing the system to dynamically create a newly redirected folder for each user to whom the policy object applies.
What different modes in windows 2003 (Mixed, native & intrim….etc)
What are the domain and forest function levels in a Windows Server 2003-basedActive Directory?
Functional levels are an extension of the mixed/native mode concept introduced in Windows 2000 to activate new Active Directory features after all the domain controllers in the domain or forest are running the Windows Server 2003 operating system.
When a computer that is running Windows Server 2003 is installed and promoted to a domain controller, new Active Directory features are activated by the Windows Server 2003 operating system over its Windows 2000 counterparts. Additional Active Directory features are available when all domain controllers in a domain or forest are running Windows Server 2003 and the administrator activates the corresponding functional level in the domain or forest.
To activate the new domain features, all domain controllers in the domain must be running Windows Server 2003. After this requirement is met, the administrator can raise the domain functional level to Windows Server 2003 (read Raise Domain Function Level in Windows Server 2003 Domains for more info).
To activate new forest-wide features, all domain controllers in the forest must be running Windows Server 2003, and the current forest functional level must be at Windows 2000 native or Windows Server 2003 domain level. After this requirement is met, the administrator can raise the domain functional level (read Raise Forest Function Level in Windows Server 2003 Active Directory for more info).
Note: Network clients can authenticate or access resources in the domain or forest without being affected by the Windows Server 2003 domain or forest functional levels. These levels only affect the way that domain controllers interact with each other.
Important
Raising the domain and forest functional levels to Windows Server 2003 is a nonreversible task and prohibits the addition of Windows NT 4.0–based or Windows 2000–based domain controllers to the environment. Any existing Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000–based domain controllers in the environment will no longer function. Before raising functional levels to take advantage of advanced Windows Server 2003 features, ensure that you will never need to install domain controllers running Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000 in your environment.
When the first Windows Server 2003–based domain controller is deployed in a domain or forest, a set of default Active Directory features becomes available. The following table summarizes the Active Directory features that are available by default on any domain controller running Windows Server 2003:
Feature Functionality
Multiple selection of user objects Allows you to modify common attributes of multiple user objects at one time.
Drag and drop functionality Allows you to move Active Directory objects from container to container by dragging one or more objects to a location in the domain hierarchy. You can also add objects to group membership lists by dragging one or more objects (including other group objects) to the target group.
Efficient search capabilities Search functionality is object-oriented and provides an efficient search that minimizes network traffic associated with browsing objects.
Saved queries Allows you to save commonly used search parameters for reuse in Active Directory Users and Computers
Active Directory command-line tools Allows you to run new directory service commands for administration scenarios.
InetOrgPerson class The inetOrgPerson class has been added to the base schema as a security principal and can be used in the same manner as the user class.
Application directory partitions Allows you to configure the replication scope for application-specific data among domain controllers. For example, you can control the replication scope of Domain Name System (DNS) zone data stored in Active Directory so that only specific domain controllers in the forest participate in DNS zone replication.
Ability to add additional domain controllers by using backup media Reduces the time it takes to add an additional domain controller in an existing domain by using backup media.
Universal group membership caching Prevents the need to locate a global catalog across a wide area network (WAN) when logging on by storing universal group membership information on an authenticating domain controller.
Secure Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) traffic Active Directory administrative tools sign and encrypt all LDAP traffic by default. Signing LDAP traffic guarantees that the packaged data comes from a known source and that it has not been tampered with.
Partial synchronization of the global catalog Provides improved replication of the global catalog when schema changes add attributes to the global catalog partial attribute set. Only the new attributes are replicated, not the entire global catalog.
Active Directory quotas Quotas can be specified in Active Directory to control the number of objects a user, group, or computer can own in a given directory partition. Members of the Domain Administrators and Enterprise Administrators groups are exempt from quotas.
When the first Windows Server 2003–based domain controller is deployed in a domain or forest, the domain or forest operates by default at the lowest functional level that is possible in that environment. This allows you to take advantage of the default Active Directory features while running versions of Windows earlier than Windows Server 2003.
When you raise the functional level of a domain or forest, a set of advanced features becomes available. For example, the Windows Server 2003 interim forest functional level supports more features than the Windows 2000 forest functional level, but fewer features than the Windows Server 2003 forest functional level supports. Windows Server 2003 is the highest functional level that is available for a domain or forest. The Windows Server 2003 functional level supports the most advanced Active Directory features; however, only Windows Server 2003 domain controllers can operate in that domain or forest.
If you raise the domain functional level to Windows Server 2003, you cannot introduce any domain controllers that are running versions of Windows earlier than Windows Server 2003 into that domain. This applies to the forest functional level as well.
Domain Functional Level
Domain functionality activates features that affect the whole domain and that domain only. The four domain functional levels, their corresponding features, and supported domain controllers are as follows:
Windows 2000 mixed (Default)
• Supported domain controllers: Microsoft Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003
• Activated features: local and global groups, global catalog support
Windows 2000 native
• Supported domain controllers: Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003
• Activated features: group nesting, universal groups, SidHistory, converting groups between security groups and distribution groups, you can raise domain levels by increasing the forest level settings
Windows Server 2003 interim
• Supported domain controllers: Windows NT 4.0, Windows Server 2003
• Supported features: There are no domain-wide features activated at this level. All domains in a forest are automatically raised to this level when the forest level increases to interim. This mode is only used when you upgrade domain controllers in Windows NT 4.0 domains to Windows Server 2003 domain controllers.
Windows Server 2003
• Supported domain controllers: Windows Server 2003
• Supported features: domain controller rename, logon timestamp attribute updated and replicated. User password support on the InetOrgPerson objectClass. Constrained delegation, you can redirect the Users and Computers containers.
Domains that are upgraded from Windows NT 4.0 or created by the promotion of a Windows Server 2003-based computer operate at the Windows 2000 mixed functional level. Windows 2000 domains maintain their current domain functional level when Windows 2000 domain controllers are upgraded to the Windows Server 2003 operating system. You can raise the domain functional level to either Windows 2000 native or Windows Server 2003.
After the domain functional level is raised, domain controllers that are running earlier operating systems cannot be introduced into the domain. For example, if you raise the domain functional level to Windows Server 2003, domain controllers that are running Windows 2000 Server cannot be added to that domain.
The following describes the domain functional level and the domain-wide features that are activated for that level. Note that with each successive level increase, the feature set of the previous level is included.
Forest Functional Level
Forest functionality activates features across all the domains in your forest. Three forest functional levels, the corresponding features, and their supported domain controllers are listed below.
Windows 2000 (default)
• Supported domain controllers: Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003
• New features: Partial list includes universal group caching, application partitions, install from media, quotas, rapid global catalog demotion, Single Instance Store (SIS) for System Access Control Lists (SACL) in the Jet Database Engine, Improved topology generation event logging. No global catalog full sync when attributes are added to the PAS Windows Server 2003 domain controller assumes the Intersite Topology Generator (ISTG) role.
Windows Server 2003 interim
• Supported domain controllers: Windows NT 4.0, Windows Server 2003. See the "Upgrade from a Windows NT 4.0 Domain" section of this article.
• Activated features: Windows 2000 features plus Efficient Group Member Replication using Linked Value Replication, Improved Replication Topology Generation. ISTG Aliveness no longer replicated. Attributes added to the global catalog. ms-DS-Trust-Forest-Trust-Info. Trust-Direction, Trust-Attributes, Trust-Type, Trust-Partner, Security-Identifier, ms-DS-Entry-Time-To-Die, Message Queuing-Secured-Source, Message Queuing-Multicast-Address, Print-Memory, Print-Rate, Print-Rate-Unit
Windows Server 2003
• Supported domain controllers: Windows Server 2003
• Activated features: all features in Interim Level, Defunct schema objects, Cross Forest Trust, Domain Rename, Dynamic auxiliary classes, InetOrgPerson objectClass change, Application Groups, 15-second intrasite replication frequency for Windows Server 2003 domain controllers upgraded from Windows 2000
After the forest functional level is raised, domain controllers that are running earlier operating systems cannot be introduced into the forest. For example, if you raise forest functional levels to Windows Server 2003, domain controllers that are running Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000 Server cannot be added to the forest.
Different Active Directory features are available at different functional levels. Raising domain and forest functional levels is required to enable certain new features as domain controllers are upgraded from Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 to Windows Server 2003
Domain Functional Levels: Windows 2000 Mixed mode, Windows 2000 Native mode, Windows server 2003 and Windows server 2003 interim ( Only available when upgrades directly from Windows NT 4.0 to Windows 2003)
Forest Functional Levels: Windows 2000 and Windows 2003
Ipsec usage and difference window 2000 & 2003.
Microsoft doesn’t recommend Internet Protocol security (IPSec) network address translation (NAT) traversal (NAT-T) for Windows deployments that include VPN servers and that are located behind network address translators. When a server is behind a network address translator, and the server uses IPSec NAT-T, unintended side effects may occur because of the way that network address translators translate network traffic
If you put a server behind a network address translator, you may experience connection problems because clients that connect to the server over the Internet require a public IP address. To reach servers that are located behind network address translators from the Internet, static mappings must be configured on the network address translator. For example, to reach a Windows Server 2003-based computer that is behind a network address translator from the Internet, configure the network address translator with the following static network address translator mappings:
• Public IP address/UDP port 500 to the server's private IP address/UDP port 500.
• Public IP address/UDP port 4500 to the server's private IP address/UDP port 4500.
These mappings are required so that all Internet Key Exchange (IKE) and IPSec NAT-T traffic that is sent to the public address of the network address translator is automatically translated and forwarded to the Windows Server 2003-based computer
How to create application partition windows 2003 and its usage?
An application directory partition is a directory partition that is replicated only to specific domain controllers. A domain controller that participates in the replication of a particular application directory partition hosts a replica of that partition. Only domain controllers running Windows Server 2003 can host a replica of an application directory partition.
Applications and services can use application directory partitions to store application-specific data. Application directory partitions can contain any type of object, except security principals. TAPI is an example of a service that stores its application-specific data in an application directory partition.
Application directory partitions are usually created by the applications that will use them to store and replicate data. For testing and troubleshooting purposes, members of the Enterprise Admins group can manually create or manage application directory partitions using the Ntdsutil command-line tool.
Is it possible to do implicit transitive forest to forest trust relationship in windows 2003?
Implicit Transitive trust will not be possible in windows 2003. Between forests we can create explicit trust
Two-way trust
One-way: incoming
One-way: Outgoing
What is universal group membership cache in windows 2003?
Information is stored locally once this option is enabled and a user attempts to log on for the first time. The domain controller obtains the universal group membership for that user from a global catalog. Once the universal group membership information is obtained, it is cached on the domain controller for that site indefinitely and is periodically refreshed. The next time that user attempts to log on, the authenticating domain controller running Windows Server 2003 will obtain the universal group membership information from its local cache without the need to contact a global catalog.
By default, the universal group membership information contained in the cache of each domain controller will be refreshed every 8 hours.
GPMC & RSOP in windows 2003?
GPMC is tool which will be used for managing group policies and will display information like how many policies applied, on which OU’s the policies applied, What are the settings enabled in each policy, Who are the users effecting by these polices, who is managing these policies. GPMC will display all the above information.
RSoP provides details about all policy settings that are configured by an Administrator, including Administrative Templates, Folder Redirection, Internet Explorer Maintenance, Security Settings, Scripts, and Group Policy Software Installation.
When policies are applied on multiple levels (for example, site, domain, domain controller, and organizational unit), the results can conflict. RSoP can help you determine a set of applied policies and their precedence (the order in which policies are applied).
Assign & Publish the applications in GP & how?
Through Group policy you can Assign and Publish the applications by creating .msi package for that application
With Assign option you can apply policy for both user and computer. If it is applied to computer then the policy will apply to user who logs on to that computer. If it is applied on user it will apply where ever he logs on to the domain. It will be appear in Start menu—Programs. Once user click the shortcut or open any document having that extension then the application install into the local machine. If any application program files missing it will automatically repair.
With Publish option you can apply only on users. It will not install automatically when any application program files are corrupted or deleted.
DFS in windows 2003?
Refer Question 17 on level 2
How to use recovery console?
The Windows 2000 Recovery Console is a command-line console that you can start from the Windows 2000 Setup program. Using the Recovery Console, you can start and stop services, format drives, read and write data on a local drive (including drives formatted to use NTFS), and perform many other administrative tasks. The Recovery Console is particularly useful if you need to repair your system by copying a file from a floppy disk or CD-ROM to your hard drive, or if you need to reconfigure a service that is preventing your computer from starting properly. Because the Recovery Console is quite powerful, it should only be used by advanced users who have a thorough knowledge of Windows 2000. In addition, you must be an administrator to use the Recovery Console.
There are two ways to start the Recovery Console:
If you are unable to start your computer, you can run the Recovery Console from your Windows 2000 Setup disks or from the Windows 2000 Professional CD (if you can start your computer from your CD-ROM drive).
As an alternative, you can install the Recovery Console on your computer to make it available in case you are unable to restart Windows 2000. You can then select the Recovery Console option from the list of available operating systems
PPTP protocol for VPN in windows 2003?
Point-to-Point-Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a networking technology that supports multiprotocol virtual private networks (VPN), enableing remote users to access corporate networks securely across the Microsoft Windows NT® Workstation, Windows® 95, and Windows 98 operating systems and other point-to-point protocol (PPP)-enabled systems to dial into a local Internet service provider to connect securely to their corporate network through the Internet
Netdom.exe is domain management tool to rename domain controller
What is the difference between Authorized DHCP and Non Authorized DHCP?
To avoid problems in the network causing by mis-configured DHCP servers, server in windows 2000 must be validate by AD before starting service to clients. If an authorized DHCP finds any DHCP server in the network it stop serving the clients
Difference between inter-site and intra-site replication. Protocols using for replication.
Intra-site replication can be done between the domain controllers in the same site. Inter-site replication can be done between two different sites over WAN links
BHS (Bridge Head Servers) is responsible for initiating replication between the sites. Inter-site replication can be done B/w BHS in one site and BHS in another site.
We can use RPC over IP or SMTP as a replication protocols where as Domain partition is not possible to replicate using SMTP
How to monitor replication
We can user Replmon tool from support tools
Brief explanation of RAID Levels
Microsoft Windows XP, Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 offer two types of disk storage: basic and dynamic.
Basic Disk Storage
Basic storage uses normal partition tables supported by MS-DOS, Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Windows 98, Microsoft Windows Millennium Edition (Me), Microsoft Windows NT, Microsoft Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP. A disk initialized for basic storage is called a basic disk. A basic disk contains basic volumes, such as primary partitions, extended partitions, and logical drives. Additionally, basic volumes include multidisk volumes that are created by using Windows NT 4.0 or earlier, such as volume sets, stripe sets, mirror sets, and stripe sets with parity. Windows XP does not support these multidisk basic volumes. Any volume sets, stripe sets, mirror sets, or stripe sets with parity must be backed up and deleted or converted to dynamic disks before you install Windows XP Professional.
Dynamic Disk Storage
Dynamic storage is supported in Windows XP Professional, Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003. A disk initialized for dynamic storage is called a dynamic disk. A dynamic disk contains dynamic volumes, such as simple volumes, spanned volumes, striped volumes, mirrored volumes, and RAID-5 volumes. With dynamic storage, you can perform disk and volume management without the need to restart Windows.
Note: Dynamic disks are not supported on portable computers or on Windows XP Home Edition-based computers.
You cannot create mirrored volumes or RAID-5 volumes on Windows XP Home Edition, Windows XP Professional, or Windows XP 64-Bit Edition-based computers. However, you can use a Windows XP Professional-based computer to create a mirrored or RAID-5 volume on remote computers that are running Windows 2000 Server, Windows 2000 Advanced Server, or Windows 2000 Datacenter Server, or the Standard, Enterprise and Data Center versions of Windows Server 2003.
Storage types are separate from the file system type. A basic or dynamic disk can contain any combination of FAT16, FAT32, or NTFS partitions or volumes.
A disk system can contain any combination of storage types. However, all volumes on the same disk must use the same storage type.
To convert a Basic Disk to a Dynamic Disk:
Use the Disk Management snap-in in Windows XP/2000/2003 to convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Log on as Administrator or as a member of the Administrators group.
2. Click Start, and then click Control Panel.
3. Click Performance and Maintenance, click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Computer Management. You can also right-click My Computer and choose Manage if you have My Computer displayed on your desktop.
4. In the left pane, click Disk Management.
5. In the lower-right pane, right-click the basic disk that you want to convert, and then click Convert to Dynamic Disk. You must right-click the gray area that contains the disk title on the left side of the Details pane.
6. Select the check box that is next to the disk that you want to convert (if it is not already selected), and then click OK.
7. Click Details if you want to view the list of volumes in the disk. Click Convert.
8. Click Yes when you are prompted to convert the disk, and then click OK.
Warning: After you convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk, local access to the dynamic disk is limited to Windows XP Professional, Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003. Additionally, after you convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk, the dynamic volumes cannot be changed back to partitions. You must first delete all dynamic volumes on the disk and then convert the dynamic disk back to a basic disk. If you want to keep your data, you must first back up the data or move it to another volume.
Dynamic Storage Terms
A volume is a storage unit made from free space on one or more disks. It can be formatted with a file system and assigned a drive letter. Volumes on dynamic disks can have any of the following layouts: simple, spanned, mirrored, striped, or RAID-5.
A simple volume uses free space from a single disk. It can be a single region on a disk or consist of multiple, concatenated regions. A simple volume can be extended within the same disk or onto additional disks. If a simple volume is extended across multiple disks, it becomes a spanned volume.
A spanned volume is created from free disk space that is linked together from multiple disks. You can extend a spanned volume onto a maximum of 32 disks. A spanned volume cannot be mirrored and is not fault-tolerant.
A striped volume is a volume whose data is interleaved across two or more physical disks. The data on this type of volume is allocated alternately and evenly to each of the physical disks. A striped volume cannot be mirrored or extended and is not fault-tolerant. Striping is also known as RAID-0.
A mirrored volume is a fault-tolerant volume whose data is duplicated on two physical disks. All of the data on one volume is copied to another disk to provide data redundancy. If one of the disks fails, the data can still be accessed from the remaining disk. A mirrored volume cannot be extended. Mirroring is also known as RAID-1.
A RAID-5 volume is a fault-tolerant volume whose data is striped across an array of three or more disks. Parity (a calculated value that can be used to reconstruct data after a failure) is also striped across the disk array. If a physical disk fails, the portion of the RAID-5 volume that was on that failed disk can be re-created from the remaining data and the parity. A RAID-5 volume cannot be mirrored or extended.
The system volume contains the hardware-specific files that are needed to load Windows (for example, Ntldr, Boot.ini, and Ntdetect.com). The system volume can be, but does not have to be, the same as the boot volume.
The boot volume contains the Windows operating system files that are located in the %Systemroot% and %Systemroot%\System32 folders. The boot volume can be, but does not have to be, the same as the system volume.
RAID 0 – Striping
RAID 1- Mirroring (minimum 2 HDD required)
RAID 5 – Striping With Parity (Minimum 3 HDD required)
RAID levels 1 and 5 only gives redundancy
What are the different backup strategies are available
Normal Backup
Incremental Backup
Differential Backup
Daily Backup
Copy Backup
What is a global catalog
Global catalog is a role, which maintains Indexes about objects. It contains full information of the objects in its own domain and partial information of the objects in other domains. Universal Group membership information will be stored in global catalog servers and replicate to all GC’s in the forest.
What is Active Directory and what is the use of it
Active directory is a directory service, which maintains the relation ship between resources and enabling them to work together. Because of AD hierarchal structure windows 2000 is more scalable, reliable. Active directory is derived from X.500 standards where information is stored is hierarchal tree like structure. Active directory depends on two Internet standards one is DNS and other is LDAP. Information in Active directory can be queried by using LDAP protocol
What is the physical and logical structure of AD?
Active directory physical structure is a hierarchal structure which fallows Forests—Trees—Domains—Child Domains—Grand Child—etc
Active directory is logically divided into 3 partitions
1.Configuration partition 2. Schema Partition 3. Domain partition 4. Application Partition (only in windows 2003 not available in windows 2000)
Out of these Configuration, Schema partitions can be replicated between the domain controllers in the in the entire forest. Where as Domain partition can be replicated between the domain controllers in the same domain
What is the process of user authentication (Kerberos V5) in windows 2000?
After giving logon credentials an encryption key will be generated which is used to encrypt the time stamp of the client machine. User name and encrypted timestamp information will be provided to domain controller for authentication. Then Domain controller based on the password information stored in AD for that user it decrypts the encrypted time stamp information. If produces time stamp matches to its time stamp. It will provide logon session key and Ticket granting ticket to client in an encryption format. Again client decrypts and if produced time stamp information is matching then it will use logon session key to logon to the domain. Ticket granting ticket will be used to generate service granting ticket when accessing network resources
What are the port numbers for Kerberos, LDAP and Global Catalog?
Kerberos – 88, LDAP – 389, Global Catalog – 3268
What is the use of LDAP (X.500 standard?)
LDAP is a directory access protocol, which is used to exchange directory information from server to clients or from server to servers
What are the problems that are generally come across DHCP?
Scope is full with IP addresses no IP’s available for new machines
If scope options are not configured properly eg default gateway
Incorrect creation of scopes etc
What is the role responsible for time synchronization?
PDC Emulator is responsible for time synchronization. Time synchronization is important because Kerberos authentication depends on time stamp information
What is TTL & how to set TTL time in DNS?
TTL is Time to Live setting used for the amount of time that the record should remain in cache when name resolution happened.
We can set TTL in SOA (start of authority record) of DNS
How to take DNS and WINS, DHCP backup
%System root%/system32/dns
%System root%/system32/WINS
%System root%/system32/DHCP
What is recovery console
Recovery console is a utility used to recover the system when it is not booting properly or not at all booting. We can perform fallowing operations from recovery console
We can copy, rename, or replace operating system files and folders
Enable or disable service or device startup the next time that start computer
Repair the file system boot sector or the Master Boot Record
Create and format partitions on drives
What is DFS & its usage
DFS is a distributed file system used to provide common environment for users to access files and folders even when they are shared in different servers physically.
There are two types of DFS domain DFS and Stand alone DFS. We cannot provide redundancy for stand alone DFS in case of failure. Domain DFS is used in a domain environment which can be accessed by /domain name/root1 (root 1 is DFS root name). Stand alone DFS can be used in workgroup environment which can be accessed through /server name/root1 (root 1 is DFS root name). Both the cases we need to create DFS root ( Which appears like a shared folder for end users) and DFS links ( A logical link which is pointing to the server where the folder is physically shared)
The maximum number of Dfs roots per server is 1.
The maximum numbers of Dfs root replicas are 31.
The maximum number of Dfs roots per domain is unlimited.
The maximum number of Dfs links or shared folders in a Dfs root is 1,000
What is RIS and what are its requirements
RIS is a remote installation service, which is used to install operation system remotely.
Client requirements
PXE DHCP-based boot ROM version 1.00 or later NIC, or a network adapter that is supported by the RIS boot disk.
Should meet minimum operating system requirements
Software Requirements
Below network services must be active on RIS server or any server in the network
Domain Name System (DNS Service)
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Active directory “Directory” service
How many root replicas can be created in DFS?
31
What is the difference between Domain DFS and Standalone DFS?
Refer question 17.
High Level
Can we establish trust relationship between two forests?
In Windows 2000 it is not possible. In Windows 2003 it is possible
What is FSMO Roles
Flexible single master operation (FSMO) roles are
Domain Naming Master
Schema Master
PDC Emulator
Infrastructure Master
RID Master
Brief all the FSMO Roles
Windows 2000/2003 Multi-Master Model
A multi-master enabled database, such as the Active Directory, provides the flexibility of allowing changes to occur at any DC in the enterprise, but it also introduces the possibility of conflicts that can potentially lead to problems once the data is replicated to the rest of the enterprise. One way Windows 2000/2003 deals with conflicting updates is by having a conflict resolution algorithm handle discrepancies in values by resolving to the DC to which changes were written last (that is, "the last writer wins"), while discarding the changes in all other DCs. Although this resolution method may be acceptable in some cases, there are times when conflicts are just too difficult to resolve using the "last writer wins" approach. In such cases, it is best to prevent the conflict from occurring rather than to try to resolve it after the fact.
For certain types of changes, Windows 2000/2003 incorporates methods to prevent conflicting Active Directory updates from occurring.
Windows 2000/2003 Single-Master Model
To prevent conflicting updates in Windows 2000/2003, the Active Directory performs updates to certain objects in a single-master fashion.
In a single-master model, only one DC in the entire directory is allowed to process updates. This is similar to the role given to a primary domain controller (PDC) in earlier versions of Windows (such as Microsoft Windows NT 4.0), in which the PDC is responsible for processing all updates in a given domain.
In a forest, there are five FSMO roles that are assigned to one or more domain controllers. The five FSMO roles are:
Schema Master:
The schema master domain controller controls all updates and modifications to the schema. Once the Schema update is complete, it is replicated from the schema master to all other DCs in the directory. To update the schema of a forest, you must have access to the schema master. There can be only one schema master in the whole forest.
Domain naming master:
The domain naming master domain controller controls the addition or removal of domains in the forest. This DC is the only one that can add or remove a domain from the directory. It can also add or remove cross references to domains in external directories. There can be only one domain naming master in the whole forest.
Infrastructure Master:
When an object in one domain is referenced by another object in another domain, it represents the reference by the GUID, the SID (for references to security principals), and the DN of the object being referenced. The infrastructure FSMO role holder is the DC responsible for updating an object's SID and distinguished name in a cross-domain object reference. At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the infrastructure master in each domain.
Note: The Infrastructure Master (IM) role should be held by a domain controller that is not a Global Catalog server (GC). If the Infrastructure Master runs on a Global Catalog server it will stop updating object information because it does not contain any references to objects that it does not hold. This is because a Global Catalog server holds a partial replica of every object in the forest. As a result, cross-domain object references in that domain will not be updated and a warning to that effect will be logged on that DC's event log. If all the domain controllers in a domain also host the global catalog, all the domain controllers have the current data, and it is not important which domain controller holds the infrastructure master role.
Relative ID (RID) Master:
The RID master is responsible for processing RID pool requests from all domain controllers in a particular domain. When a DC creates a security principal object such as a user or group, it attaches a unique Security ID (SID) to the object. This SID consists of a domain SID (the same for all SIDs created in a domain), and a relative ID (RID) that is unique for each security principal SID created in a domain. Each DC in a domain is allocated a pool of RIDs that it is allowed to assign to the security principals it creates. When a DC's allocated RID pool falls below a threshold, that DC issues a request for additional RIDs to the domain's RID master. The domain RID master responds to the request by retrieving RIDs from the domain's unallocated RID pool and assigns them to the pool of the requesting DC. At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the RID master in the domain.
PDC Emulator:
The PDC emulator is necessary to synchronize time in an enterprise. Windows 2000/2003 includes the W32Time (Windows Time) time service that is required by the Kerberos authentication protocol. All Windows 2000/2003-based computers within an enterprise use a common time. The purpose of the time service is to ensure that the Windows Time service uses a hierarchical relationship that controls authority and does not permit loops to ensure appropriate common time usage.
The PDC emulator of a domain is authoritative for the domain. The PDC emulator at the root of the forest becomes authoritative for the enterprise, and should be configured to gather the time from an external source. All PDC FSMO role holders follow the hierarchy of domains in the selection of their in-bound time partner.
In a Windows 2000/2003 domain, the PDC emulator role holder retains the following functions:
Password changes performed by other DCs in the domain are replicated preferentially to the PDC emulator.
Authentication failures that occur at a given DC in a domain because of an incorrect password are forwarded to the PDC emulator before a bad password failure message is reported to the user.
Account lockout is processed on the PDC emulator.
Editing or creation of Group Policy Objects (GPO) is always done from the GPO copy found in the PDC Emulator's SYSVOL share, unless configured not to do so by the administrator.
The PDC emulator performs all of the functionality that a Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 Server-based PDC or earlier PDC performs for Windows NT 4.0-based or earlier clients.
This part of the PDC emulator role becomes unnecessary when all workstations, member servers, and domain controllers that are running Windows NT 4.0 or earlier are all upgraded to Windows 2000/2003. The PDC emulator still performs the other functions as described in a Windows 2000/2003 environment.
At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the PDC emulator master in each domain in the forest.
How to manually configure FSMO Roles to separate DC’s
How can I determine who are the current FSMO Roles holders in my domain/forest?
Windows 2000/2003 Active Directory domains utilize a Single Operation Master method called FSMO (Flexible Single Master Operation), as described in Understanding FSMO Roles in Active Directory.
The five FSMO roles are:
• Schema master - Forest-wide and one per forest.
• Domain naming master - Forest-wide and one per forest.
• RID master - Domain-specific and one for each domain.
• PDC - PDC Emulator is domain-specific and one for each domain.
• Infrastructure master - Domain-specific and one for each domain.
In most cases an administrator can keep the FSMO role holders (all 5 of them) in the same spot (or actually, on the same DC) as has been configured by the Active Directory installation process. However, there are scenarios where an administrator would want to move one or more of the FSMO roles from the default holder DC to a different DC. The transferring method is described in the Transferring FSMO Roles article, while seizing the roles from a non-operational DC to a different DC is described in the Seizing FSMO Roles article.
In order to better understand your AD infrastructure and to know the added value that each DC might possess, an AD administrator must have the exact knowledge of which one of the existing DCs is holding a FSMO role, and what role it holds. With that knowledge in hand, the administrator can make better arrangements in case of a scheduled shut-down of any given DC, and better prepare him or herself in case of a non-scheduled cease of operation from one of the DCs.
How to find out which DC is holding which FSMO role? Well, one can accomplish this task by many means. This article will list a few of the available methods.
Method #1: Know the default settings
The FSMO roles were assigned to one or more DCs during the DCPROMO process. The following table summarizes the FSMO default locations:
FSMO Role Number of DCs holding this role Original DC holding the FSMO role
Schema One per forest The first DC in the first domain in the forest (i.e. the Forest Root Domain)
Domain Naming One per forest
RID One per domain The first DC in a domain (any domain, including the Forest Root Domain, any Tree Root Domain, or any Child Domain)
PDC Emulator One per domain
Infrastructure One per domain
Method #2: Use the GUI
The FSMO role holders can be easily found by use of some of the AD snap-ins. Use this table to see which tool can be used for what FSMO role:
FSMO Role Which snap-in should I use?
Schema Schema snap-in
Domain Naming AD Domains and Trusts snap-in
RID AD Users and Computers snap-in
PDC Emulator
Infrastructure
Finding the RID Master, PDC Emulator, and Infrastructure Masters via GUI
To find out who currently holds the Domain-Specific RID Master, PDC Emulator, and Infrastructure Master FSMO Roles:
1. Open the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in from the Administrative Tools folder.
2. Right-click the Active Directory Users and Computers icon again and press Operation Masters.
3. Select the appropriate tab for the role you wish to view.
4. When you're done click close.
Finding the Domain Naming Master via GUI
To find out who currently holds the Domain Naming Master Role:
1. Open the Active Directory Domains and Trusts snap-in from the Administrative Tools folder.
2. Right-click the Active Directory Domains and Trusts icon again and press Operation Masters.
3. When you're done click close.
Finding the Schema Master via GUI
To find out who currently holds the Schema Master Role:
1. Register the Schmmgmt.dll library by pressing Start > RUN and typing:
2. Press OK. You should receive a success confirmation.
3. From the Run command open an MMC Console by typing MMC.
4. On the Console menu, press Add/Remove Snap-in.
5. Press Add. Select Active Directory Schema.
6. Press Add and press Close. Press OK.
7. Click the Active Directory Schema icon. After it loads right-click it and press Operation Masters.
8. Press the Close button.
Method #3: Use the Ntdsutil command
The FSMO role holders can be easily found by use of the Ntdsutil command.
Caution: Using the Ntdsutil utility incorrectly may result in partial or complete loss of Active Directory functionality.
1. On any domain controller, click Start, click Run, type Ntdsutil in the Open box, and then click OK.
2. Type roles, and then press ENTER.
Note: To see a list of available commands at any of the prompts in the Ntdsutil tool, type ?, and then press ENTER.
3. Type connections, and then press ENTER.
4. Type connect to server , where is the name of the server you want to use, and then press ENTER.
5. At the server connections: prompt, type q, and then press ENTER again.
6. At the FSMO maintenance: prompt, type Select operation target, and then press ENTER again.
At the select operation target: prompt, type List roles for connected server, and then press ENTER again.
select operation target: List roles for connected server
Server "server100" knows about 5 roles
Schema - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=C
onfiguration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
Domain - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=C
onfiguration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
PDC - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Conf
iguration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
RID - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Conf
iguration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
Infrastructure - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Si
tes,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
select operation target:
8. Type q 3 times to exit the Ntdsutil prompt.
Note: You can download THIS nice batch file that will do all this for you (1kb).
Another Note: Microsoft has a nice tool called Dumpfsmos.cmd, found in the Windows 2000 Resource Kit (and can be downloaded here: Download Free Windows 2000 Resource Kit Tools). This tool is basically a one-click Ntdsutil script that performs the same operation described above.
Method #4: Use the Netdom command
The FSMO role holders can be easily found by use of the Netdom command.
Netdom.exe is a part of the Windows 2000/XP/2003 Support Tools. You must either download it separately (from here Download Free Windows 2000 Resource Kit Tools) or by obtaining the correct Support Tools pack for your operating system. The Support Tools pack can be found in the \Support\Tools folder on your installation CD (or you can Download Windows 2000 SP4 Support Tools, Download Windows XP SP1 Deploy Tools).
1. On any domain controller, click Start, click Run, type CMD in the Open box, and then click OK.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type netdom query /domain: fsmo (where is the name of YOUR domain).
Close the CMD window.
Note: You can download THIS nice batch file that will do all this for you (1kb).
Method #5: Use the Replmon tool
The FSMO role holders can be easily found by use of the Netdom command.
Just like Netdom, Replmon.exe is a part of the Windows 2000/XP/2003 Support Tools. Replmon can be used for a wide verity of tasks, mostly with those that are related with AD replication. But Replmon can also provide valuable information about the AD, about any DC, and also about other objects and settings, such as GPOs and FSMO roles. Install the package before attempting to use the tool.
1. On any domain controller, click Start, click Run, type REPLMON in the Open box, and then click OK.
2. Right-click Monitored servers and select Add Monitored Server.
3. In the Add Server to Monitor window, select the Search the Directory for the server to add. Make sure your AD domain name is listed in the drop-down list.
4. In the site list select your site, expand it, and click to select the server you want to query. Click Finish.
5. Right-click the server that is now listed in the left-pane, and select Properties.
6. Click on the FSMO Roles tab and read the results.
7. Click Ok when you're done.
How can I forcibly transfer (seize) some or all of the FSMO Roles from one DC to another?
Windows 2000/2003 Active Directory domains utilize a Single Operation Master method called FSMO (Flexible Single Master Operation), as described in Understanding FSMO Roles in Active Directory.
The five FSMO roles are:
• Schema master - Forest-wide and one per forest.
• Domain naming master - Forest-wide and one per forest.
• RID master - Domain-specific and one for each domain.
• PDC - PDC Emulator is domain-specific and one for each domain.
• Infrastructure master - Domain-specific and one for each domain.
In most cases an administrator can keep the FSMO role holders (all 5 of them) in the same spot (or actually, on the same DC) as has been configured by the Active Directory installation process. However, there are scenarios where an administrator would want to move one or more of the FSMO roles from the default holder DC to a different DC.
Moving the FSMO roles while both the original FSMO role holder and the future FSMO role holder are online and operational is called Transferring, and is described in the Transferring FSMO Roles article.
However, when the original FSMO role holder went offline or became non operational for a long period of time, the administrator might consider moving the FSMO role from the original, non-operational holder, to a different DC. The process of moving the FSMO role from a non-operational role holder to a different DC is called Seizing, and is described in this article.
If a DC holding a FSMO role fails, the best thing to do is to try and get the server online again. Since none of the FSMO roles are immediately critical (well, almost none, the loss of the PDC Emulator FSMO role might become a problem unless you fix it in a reasonable amount of time), so it is not a problem to them to be unavailable for hours or even days.
If a DC becomes unreliable, try to get it back on line, and transfer the FSMO roles to a reliable computer. Administrators should use extreme caution in seizing FSMO roles. This operation, in most cases, should be performed only if the original FSMO role owner will not be brought back into the environment. Only seize a FSMO role if absolutely necessary when the original role holder is not connected to the network.
What will happen if you do not perform the seize in time? This table has the info:
FSMO Role Loss implications
Schema The schema cannot be extended. However, in the short term no one will notice a missing Schema Master unless you plan a schema upgrade during that time.
Domain Naming Unless you are going to run DCPROMO, then you will not miss this FSMO role.
RID Chances are good that the existing DCs will have enough unused RIDs to last some time, unless you're building hundreds of users or computer object per week.
PDC Emulator Will be missed soon. NT 4.0 BDCs will not be able to replicate, there will be no time synchronization in the domain, you will probably not be able to change or troubleshoot group policies and password changes will become a problem.
Infrastructure Group memberships may be incomplete. If you only have one domain, then there will be no impact.
Important: If the RID, Schema, or Domain Naming FSMOs are seized, then the original domain controller must not be activated in the forest again. It is necessary to reinstall Windows if these servers are to be used again.
The following table summarizes the FSMO seizing restrictions:
FSMO Role Restrictions
Schema Original must be reinstalled
Domain Naming
RID
PDC Emulator Can transfer back to original
Infrastructure
Another consideration before performing the seize operation is the administrator's group membership, as this table lists:
FSMO Role Administrator must be a member of
Schema Schema Admins
Domain Naming Enterprise Admins
RID Domain Admins
PDC Emulator
Infrastructure
To seize the FSMO roles by using Ntdsutil, follow these steps:
Caution: Using the Ntdsutil utility incorrectly may result in partial or complete loss of Active Directory functionality.
1. On any domain controller, click Start, click Run, type Ntdsutil in the Open box, and then click OK.
2. Type roles, and then press ENTER.
Note: To see a list of available commands at any of the prompts in the Ntdsutil tool, type ?, and then press ENTER.
3. Type connections, and then press ENTER.
4. Type connect to server , where is the name of the server you want to use, and then press ENTER.
5. At the server connections: prompt, type q, and then press ENTER again.
6. Type seize , where is the role you want to seize. For example, to seize the RID Master role, you would type seize rid master:
Options are:
7. You will receive a warning window asking if you want to perform the seize. Click on Yes.
fsmo maintenance: Seize infrastructure master
Attempting safe transfer of infrastructure FSMO before seizure.
ldap_modify_sW error 0x34(52 (Unavailable).
Ldap extended error message is 000020AF: SvcErr: DSID-03210300, problem 5002 (UNAVAILABLE)
data 1722
Win32 error returned is 0x20af(The requested FSMO operation failed. The current FSMO holde
r could not be contacted.)
)
Depending on the error code this may indicate a connection,
ldap, or role transfer error.
Transfer of infrastructure FSMO failed, proceeding with seizure ...
Server "server100" knows about 5 roles
Schema - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER200,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=netDomain - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
PDC - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
RID - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER200,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
Infrastructure - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dpetri,DC=net
fsmo maintenance:
Note: All five roles need to be in the forest. If the first domain controller is out of the forest then seize all roles. Determine which roles are to be on which remaining domain controllers so that all five roles are not on only one server.
8. Repeat steps 6 and 7 until you've seized all the required FSMO roles.
9. After you seize or transfer the roles, type q, and then press ENTER until you quit the Ntdsutil tool.
Note: Do not put the Infrastructure Master (IM) role on the same domain controller as the Global Catalog server. If the Infrastructure Master runs on a GC server it will stop updating object information because it does not contain any references to objects that it does not hold. This is because a GC server holds a partial replica of every object in the forest.
What is the difference between authoritative and non-authoritative restore
In authoritative restore, Objects that are restored will be replicated to all domain controllers in the domain. This can be used specifically when the entire OU is disturbed in all domain controllers or specifically restore a single object, which is disturbed in all DC’s
In non-authoritative restore, Restored directory information will be updated by other domain controllers based on the latest modification time.
What is Active Directory De-fragmentation?
De-fragmentation of AD means separating used space and empty space created by deleted objects and reduces directory size (only in offline De-fragmentation)
Difference between online and offline de-fragmentation
The size of NTDS.DIT will often be different sizes across the domain controllers in a domain. Remember that Active Directory is a multi-master independent model where updates are occurring in each of the domain controllers with the changes being replicated over time to the other domain controllers.
The changed data is replicated between domain controllers, not the database, so there is no guarantee that the files are going to be the same size across all domain controllers.
Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 servers running Directory Services (DS) perform a directory online defragmentation every 12 hours by default as part of the garbage-collection process. This defragmentation only moves data around the database file (NTDS.DIT) and doesn’t reduce the file’s size - the database file cannot be compacted while Active Directory is mounted.
Active Directory routinely performs online database defragmentation, but this is limited to the disposal of tombstoned objects. The database file cannot be compacted while Active Directory is mounted (or online).
An NTDS.DIT file that has been defragmented offline (compacted), can be much smaller than the NTDS.DIT file on its peers.
However, defragmenting the NTDS.DIT file isn’t something you should really need to do. Normally, the database self-tunes and automatically tombstoning the records then sweeping them away when the tombstone lifetime has passed to make that space available for additional records.
Defragging the NTDS.DIT file probably won’t help your AD queries go any faster in the long run.
So why defrag it in the first place?
One reason you might want to defrag your NTDS.DIT file is to save space, for example if you deleted a large number of records at one time.
To create a new, smaller NTDS.DIT file and to enable offline defragmentation, perform the following steps:
Back up Active Directory (AD).
Reboot the server, select the OS option, and press F8 for advanced options.
Select the Directory Services Restore Mode option, and press Enter. Press
Enter again to start the OS.
W2K will start in safe mode, with no DS running.
Use the local SAM’s administrator account and password to log on.
You’ll see a dialog box that says you’re in safe mode. Click OK.
From the Start menu, select Run and type cmd.exe
In the command window, you’ll see the following text. (Enter the commands in bold.)
C:\> ntdsutil
ntdsutil: files
file maintenance:info
....
file maintenance:compact to c:\temp
You’ll see the defragmentation process. If the process was successful, enter quit to return to the command prompt.
Then, replace the old NTDS.DIT file with the new, compressed version. (Enter the commands in bold.)
C:\> copy c:\temp\ntds.dit %systemroot%\ntds\ntds.dit
Restart the computer, and boot as normal.
What is tombstone period
Tombstones are nothing but objects marked for deletion. After deleting an object in AD the objects will not be deleted permanently. It will be remain 60 days by default (which can be configurable) it adds an entry as marked for deletion on the object and replicates to all DC’s. After 60 days object will be deleted permanently from all Dc’s.
What is white space and Garbage Collection?
refer question 7
What are the monitoring tools used for Server and Network Heath. How to define alert mechanism
Spot Light , SNMP Need to enable .
How to deploy the patches and what are the softwares used for this process
Using SUS (Software update services) server we can deploy patches to all clients in the network. We need to configure an option called “Synchronize with Microsoft software update server” option and schedule time to synchronize in server. We need to approve new update based on the requirement. Then approved update will be deployed to clients
We can configure clients by changing the registry manually or through Group policy by adding WUAU administrative template in group policy
What is Clustering. Briefly define & explain it
Clustering is a technology, which is used to provide High Availability for mission critical applications. We can configure cluster by installing MCS (Microsoft cluster service) component from Add remove programs, which can only available in Enterprise Edition and Data center edition.
In Windows we can configure two types of clusters
NLB (network load balancing) cluster for balancing load between servers. This cluster will not provide any high availability. Usually preferable at edge servers like web or proxy.
Server Cluster: This provides High availability by configuring active-active or active-passive cluster. In 2 node active-passive cluster one node will be active and one node will be stand by. When active server fails the application will FAILOVER to stand by server automatically. When the original server backs we need to FAILBACK the application
Quorum: A shared storage need to provide for all servers which keeps information about clustered application and session state and is useful in FAILOVER situation. This is very important if Quorum disk fails entire cluster will fails
Heartbeat: Heartbeat is a private connectivity between the servers in the cluster, which is used to identify the status of other servers in cluster.
How to configure SNMP
SNMP can be configured by installing SNMP from Monitoring and Management tools from Add and Remove programs.
For SNMP programs to communicate we need to configure common community name for those machines where SNMP programs (eg DELL OPEN MANAGER) running. This can be configured from services.msc--- SNMP service -- Security
Is it possible to rename the Domain name & how?
In Windows 2000 it is not possible. In windows 2003 it is possible. On Domain controller by going to MYCOMPUTER properties we can change.
What is SOA Record
SOA is a Start Of Authority record, which is a first record in DNS, which controls the startup behavior of DNS. We can configure TTL, refresh, and retry intervals in this record.
What is a Stub zone and what is the use of it.
Stub zones are a new feature of DNS in Windows Server 2003 that can be used to streamline name resolution, especially in a split namespace scenario. They also help reduce the amount of DNS traffic on your network, making DNS more efficient especially over slow WAN links.
What are the different types of partitions present in AD?
Active directory is divided into three partitions
Configuration Partition—replicates entire forest
Schema Partition—replicates entire forest
Domain Partition—replicate only in domain
Application Partition (Only in Windows 2003)
What are the (two) services required for replication
File Replication Service (FRS)
Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC)
Can we use a Linux DNS Sever in 2000 Domain?
We can use, But the BIND version should be 8 or greater
What is the difference between IIS Version 5 and IIS Version 6?
Refer Question 1
What is ASR (Automated System Recovery) and how to implement it
ASR is a two-part system; it includes ASR backup and ASR restore. The ASR Wizard, located in Backup, does the backup portion. The wizard backs up the system state, system services, and all the disks that are associated with the operating system components. ASR also creates a file that contains information about the backup, the disk configurations (including basic and dynamic volumes), and how to perform a restore.
You can access the restore portion by pressing F2 when prompted in the text-mode portion of setup. ASR reads the disk configurations from the file that it creates. It restores all the disk signatures, volumes, and partitions on (at a minimum) the disks that you need to start the computer. ASR will try to restore all the disk configurations, but under some circumstances it might not be able to. ASR then installs a simple installation of Windows and automatically starts a restoration using the backup created by the ASR Wizard.
What are the different levels that we can apply Group Policy
We can apply group policy at SITE level---Domain Level---OU level
What is Domain Policy, Domain controller policy, Local policy and Group policy
Domain Policy will apply to all computers in the domain, because by default it will be associated with domain GPO, Where as Domain controller policy will be applied only on domain controller. By default domain controller security policy will be associated with domain controller GPO. Local policy will be applied to that particular machine only and effects to that computer only.
What is the use of SYSVOL FOLDER?
Policies and scripts saved in SYSVOL folder will be replicated to all domain controllers in the domain. FRS (File replication service) is responsible for replicating all policies and scripts
What is folder redirection?
Folder Redirection is a User group policy. Once you create the group policy and link it to the appropriate folder object, an administrator can designate which folders to redirect and where To do this, the administrator needs to navigate to the following location in the Group Policy Object:
User Configuration\Windows Settings\Folder Redirection
In the Properties of the folder, you can choose Basic or Advanced folder redirection, and you can designate the server file system path to which the folder should be redirected.
The %USERNAME% variable may be used as part of the redirection path, thus allowing the system to dynamically create a newly redirected folder for each user to whom the policy object applies.
What different modes in windows 2003 (Mixed, native & intrim….etc)
What are the domain and forest function levels in a Windows Server 2003-basedActive Directory?
Functional levels are an extension of the mixed/native mode concept introduced in Windows 2000 to activate new Active Directory features after all the domain controllers in the domain or forest are running the Windows Server 2003 operating system.
When a computer that is running Windows Server 2003 is installed and promoted to a domain controller, new Active Directory features are activated by the Windows Server 2003 operating system over its Windows 2000 counterparts. Additional Active Directory features are available when all domain controllers in a domain or forest are running Windows Server 2003 and the administrator activates the corresponding functional level in the domain or forest.
To activate the new domain features, all domain controllers in the domain must be running Windows Server 2003. After this requirement is met, the administrator can raise the domain functional level to Windows Server 2003 (read Raise Domain Function Level in Windows Server 2003 Domains for more info).
To activate new forest-wide features, all domain controllers in the forest must be running Windows Server 2003, and the current forest functional level must be at Windows 2000 native or Windows Server 2003 domain level. After this requirement is met, the administrator can raise the domain functional level (read Raise Forest Function Level in Windows Server 2003 Active Directory for more info).
Note: Network clients can authenticate or access resources in the domain or forest without being affected by the Windows Server 2003 domain or forest functional levels. These levels only affect the way that domain controllers interact with each other.
Important
Raising the domain and forest functional levels to Windows Server 2003 is a nonreversible task and prohibits the addition of Windows NT 4.0–based or Windows 2000–based domain controllers to the environment. Any existing Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000–based domain controllers in the environment will no longer function. Before raising functional levels to take advantage of advanced Windows Server 2003 features, ensure that you will never need to install domain controllers running Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000 in your environment.
When the first Windows Server 2003–based domain controller is deployed in a domain or forest, a set of default Active Directory features becomes available. The following table summarizes the Active Directory features that are available by default on any domain controller running Windows Server 2003:
Feature Functionality
Multiple selection of user objects Allows you to modify common attributes of multiple user objects at one time.
Drag and drop functionality Allows you to move Active Directory objects from container to container by dragging one or more objects to a location in the domain hierarchy. You can also add objects to group membership lists by dragging one or more objects (including other group objects) to the target group.
Efficient search capabilities Search functionality is object-oriented and provides an efficient search that minimizes network traffic associated with browsing objects.
Saved queries Allows you to save commonly used search parameters for reuse in Active Directory Users and Computers
Active Directory command-line tools Allows you to run new directory service commands for administration scenarios.
InetOrgPerson class The inetOrgPerson class has been added to the base schema as a security principal and can be used in the same manner as the user class.
Application directory partitions Allows you to configure the replication scope for application-specific data among domain controllers. For example, you can control the replication scope of Domain Name System (DNS) zone data stored in Active Directory so that only specific domain controllers in the forest participate in DNS zone replication.
Ability to add additional domain controllers by using backup media Reduces the time it takes to add an additional domain controller in an existing domain by using backup media.
Universal group membership caching Prevents the need to locate a global catalog across a wide area network (WAN) when logging on by storing universal group membership information on an authenticating domain controller.
Secure Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) traffic Active Directory administrative tools sign and encrypt all LDAP traffic by default. Signing LDAP traffic guarantees that the packaged data comes from a known source and that it has not been tampered with.
Partial synchronization of the global catalog Provides improved replication of the global catalog when schema changes add attributes to the global catalog partial attribute set. Only the new attributes are replicated, not the entire global catalog.
Active Directory quotas Quotas can be specified in Active Directory to control the number of objects a user, group, or computer can own in a given directory partition. Members of the Domain Administrators and Enterprise Administrators groups are exempt from quotas.
When the first Windows Server 2003–based domain controller is deployed in a domain or forest, the domain or forest operates by default at the lowest functional level that is possible in that environment. This allows you to take advantage of the default Active Directory features while running versions of Windows earlier than Windows Server 2003.
When you raise the functional level of a domain or forest, a set of advanced features becomes available. For example, the Windows Server 2003 interim forest functional level supports more features than the Windows 2000 forest functional level, but fewer features than the Windows Server 2003 forest functional level supports. Windows Server 2003 is the highest functional level that is available for a domain or forest. The Windows Server 2003 functional level supports the most advanced Active Directory features; however, only Windows Server 2003 domain controllers can operate in that domain or forest.
If you raise the domain functional level to Windows Server 2003, you cannot introduce any domain controllers that are running versions of Windows earlier than Windows Server 2003 into that domain. This applies to the forest functional level as well.
Domain Functional Level
Domain functionality activates features that affect the whole domain and that domain only. The four domain functional levels, their corresponding features, and supported domain controllers are as follows:
Windows 2000 mixed (Default)
• Supported domain controllers: Microsoft Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003
• Activated features: local and global groups, global catalog support
Windows 2000 native
• Supported domain controllers: Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003
• Activated features: group nesting, universal groups, SidHistory, converting groups between security groups and distribution groups, you can raise domain levels by increasing the forest level settings
Windows Server 2003 interim
• Supported domain controllers: Windows NT 4.0, Windows Server 2003
• Supported features: There are no domain-wide features activated at this level. All domains in a forest are automatically raised to this level when the forest level increases to interim. This mode is only used when you upgrade domain controllers in Windows NT 4.0 domains to Windows Server 2003 domain controllers.
Windows Server 2003
• Supported domain controllers: Windows Server 2003
• Supported features: domain controller rename, logon timestamp attribute updated and replicated. User password support on the InetOrgPerson objectClass. Constrained delegation, you can redirect the Users and Computers containers.
Domains that are upgraded from Windows NT 4.0 or created by the promotion of a Windows Server 2003-based computer operate at the Windows 2000 mixed functional level. Windows 2000 domains maintain their current domain functional level when Windows 2000 domain controllers are upgraded to the Windows Server 2003 operating system. You can raise the domain functional level to either Windows 2000 native or Windows Server 2003.
After the domain functional level is raised, domain controllers that are running earlier operating systems cannot be introduced into the domain. For example, if you raise the domain functional level to Windows Server 2003, domain controllers that are running Windows 2000 Server cannot be added to that domain.
The following describes the domain functional level and the domain-wide features that are activated for that level. Note that with each successive level increase, the feature set of the previous level is included.
Forest Functional Level
Forest functionality activates features across all the domains in your forest. Three forest functional levels, the corresponding features, and their supported domain controllers are listed below.
Windows 2000 (default)
• Supported domain controllers: Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003
• New features: Partial list includes universal group caching, application partitions, install from media, quotas, rapid global catalog demotion, Single Instance Store (SIS) for System Access Control Lists (SACL) in the Jet Database Engine, Improved topology generation event logging. No global catalog full sync when attributes are added to the PAS Windows Server 2003 domain controller assumes the Intersite Topology Generator (ISTG) role.
Windows Server 2003 interim
• Supported domain controllers: Windows NT 4.0, Windows Server 2003. See the "Upgrade from a Windows NT 4.0 Domain" section of this article.
• Activated features: Windows 2000 features plus Efficient Group Member Replication using Linked Value Replication, Improved Replication Topology Generation. ISTG Aliveness no longer replicated. Attributes added to the global catalog. ms-DS-Trust-Forest-Trust-Info. Trust-Direction, Trust-Attributes, Trust-Type, Trust-Partner, Security-Identifier, ms-DS-Entry-Time-To-Die, Message Queuing-Secured-Source, Message Queuing-Multicast-Address, Print-Memory, Print-Rate, Print-Rate-Unit
Windows Server 2003
• Supported domain controllers: Windows Server 2003
• Activated features: all features in Interim Level, Defunct schema objects, Cross Forest Trust, Domain Rename, Dynamic auxiliary classes, InetOrgPerson objectClass change, Application Groups, 15-second intrasite replication frequency for Windows Server 2003 domain controllers upgraded from Windows 2000
After the forest functional level is raised, domain controllers that are running earlier operating systems cannot be introduced into the forest. For example, if you raise forest functional levels to Windows Server 2003, domain controllers that are running Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000 Server cannot be added to the forest.
Different Active Directory features are available at different functional levels. Raising domain and forest functional levels is required to enable certain new features as domain controllers are upgraded from Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000 to Windows Server 2003
Domain Functional Levels: Windows 2000 Mixed mode, Windows 2000 Native mode, Windows server 2003 and Windows server 2003 interim ( Only available when upgrades directly from Windows NT 4.0 to Windows 2003)
Forest Functional Levels: Windows 2000 and Windows 2003
Ipsec usage and difference window 2000 & 2003.
Microsoft doesn’t recommend Internet Protocol security (IPSec) network address translation (NAT) traversal (NAT-T) for Windows deployments that include VPN servers and that are located behind network address translators. When a server is behind a network address translator, and the server uses IPSec NAT-T, unintended side effects may occur because of the way that network address translators translate network traffic
If you put a server behind a network address translator, you may experience connection problems because clients that connect to the server over the Internet require a public IP address. To reach servers that are located behind network address translators from the Internet, static mappings must be configured on the network address translator. For example, to reach a Windows Server 2003-based computer that is behind a network address translator from the Internet, configure the network address translator with the following static network address translator mappings:
• Public IP address/UDP port 500 to the server's private IP address/UDP port 500.
• Public IP address/UDP port 4500 to the server's private IP address/UDP port 4500.
These mappings are required so that all Internet Key Exchange (IKE) and IPSec NAT-T traffic that is sent to the public address of the network address translator is automatically translated and forwarded to the Windows Server 2003-based computer
How to create application partition windows 2003 and its usage?
An application directory partition is a directory partition that is replicated only to specific domain controllers. A domain controller that participates in the replication of a particular application directory partition hosts a replica of that partition. Only domain controllers running Windows Server 2003 can host a replica of an application directory partition.
Applications and services can use application directory partitions to store application-specific data. Application directory partitions can contain any type of object, except security principals. TAPI is an example of a service that stores its application-specific data in an application directory partition.
Application directory partitions are usually created by the applications that will use them to store and replicate data. For testing and troubleshooting purposes, members of the Enterprise Admins group can manually create or manage application directory partitions using the Ntdsutil command-line tool.
Is it possible to do implicit transitive forest to forest trust relationship in windows 2003?
Implicit Transitive trust will not be possible in windows 2003. Between forests we can create explicit trust
Two-way trust
One-way: incoming
One-way: Outgoing
What is universal group membership cache in windows 2003?
Information is stored locally once this option is enabled and a user attempts to log on for the first time. The domain controller obtains the universal group membership for that user from a global catalog. Once the universal group membership information is obtained, it is cached on the domain controller for that site indefinitely and is periodically refreshed. The next time that user attempts to log on, the authenticating domain controller running Windows Server 2003 will obtain the universal group membership information from its local cache without the need to contact a global catalog.
By default, the universal group membership information contained in the cache of each domain controller will be refreshed every 8 hours.
GPMC & RSOP in windows 2003?
GPMC is tool which will be used for managing group policies and will display information like how many policies applied, on which OU’s the policies applied, What are the settings enabled in each policy, Who are the users effecting by these polices, who is managing these policies. GPMC will display all the above information.
RSoP provides details about all policy settings that are configured by an Administrator, including Administrative Templates, Folder Redirection, Internet Explorer Maintenance, Security Settings, Scripts, and Group Policy Software Installation.
When policies are applied on multiple levels (for example, site, domain, domain controller, and organizational unit), the results can conflict. RSoP can help you determine a set of applied policies and their precedence (the order in which policies are applied).
Assign & Publish the applications in GP & how?
Through Group policy you can Assign and Publish the applications by creating .msi package for that application
With Assign option you can apply policy for both user and computer. If it is applied to computer then the policy will apply to user who logs on to that computer. If it is applied on user it will apply where ever he logs on to the domain. It will be appear in Start menu—Programs. Once user click the shortcut or open any document having that extension then the application install into the local machine. If any application program files missing it will automatically repair.
With Publish option you can apply only on users. It will not install automatically when any application program files are corrupted or deleted.
DFS in windows 2003?
Refer Question 17 on level 2
How to use recovery console?
The Windows 2000 Recovery Console is a command-line console that you can start from the Windows 2000 Setup program. Using the Recovery Console, you can start and stop services, format drives, read and write data on a local drive (including drives formatted to use NTFS), and perform many other administrative tasks. The Recovery Console is particularly useful if you need to repair your system by copying a file from a floppy disk or CD-ROM to your hard drive, or if you need to reconfigure a service that is preventing your computer from starting properly. Because the Recovery Console is quite powerful, it should only be used by advanced users who have a thorough knowledge of Windows 2000. In addition, you must be an administrator to use the Recovery Console.
There are two ways to start the Recovery Console:
If you are unable to start your computer, you can run the Recovery Console from your Windows 2000 Setup disks or from the Windows 2000 Professional CD (if you can start your computer from your CD-ROM drive).
As an alternative, you can install the Recovery Console on your computer to make it available in case you are unable to restart Windows 2000. You can then select the Recovery Console option from the list of available operating systems
PPTP protocol for VPN in windows 2003?
Point-to-Point-Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a networking technology that supports multiprotocol virtual private networks (VPN), enableing remote users to access corporate networks securely across the Microsoft Windows NT® Workstation, Windows® 95, and Windows 98 operating systems and other point-to-point protocol (PPP)-enabled systems to dial into a local Internet service provider to connect securely to their corporate network through the Internet
Netdom.exe is domain management tool to rename domain controller
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)